C++ Basic (2)
1. delete[]
A *pA = new A[5]; |
上述代码调用了5次构造函数, 一次析构函数. 因为delete只会析构一个元素, 也就是数组第一个元素. 所以应调用delete[]来删除数组中的所有对象
2. for loop
for有两种语法:
for (init-statement condition; iteration-expression)for (declaration-or-expression; declaration-or-expression; expression)
上述所有expression和statement都是可选的, 也就是说, 特定情况下我们可选择不填写, 如下:
for(expression1 ; ; expression2) |
相当于
for(expression1 ; 1 ; expression2) |
等同while(true).
3. preprocessor
preprocessor directives
用于简化源程序在不同的执行环境中的更改和编译/*
* #include, #using, #import, #error
* #define, #undef
* #if, #else, #ifdef, #ifndef, #elif, #endif
* #line, #pragma
*/preprocessor operators
- 字符串化运算符(
#) - 字符化运算符(
#@) - 标记粘贴运算符(
##) - 自定义的运算符
- 字符串化运算符(
preprocessor macros
__DATE__: 当前的编译日期__FILE__: 当前源文件名__LINE__: 当前源代码行号__STDC__: 当要求程序严格遵循ANSI C标准时该标识被赋值为1__STDCPP_THREADS__: 多个线程的执行且为C++编译时赋值为1__TIME__: 当前编译时间
pragmas: 设定编译器的状态或指示编译器做某些特定动作, 支持多种参数
4. Static Binding
对于非虚成员函数, C++采用静态绑定.
class B |
pD->Do()和pB->Do()调用的是各自的函数, 因为绑定的静态类型不同- 虚函数使用dynamic binding(动态绑定)确定调用哪个函数, 所以
pD->vfun()和pB->vfun()相同, 都是调用的D::vfun()
5. printf
float k = 0.8567; |
6. Integral Promotion
执行表达式计算时(包括比较运算和算术运算等), 比int类型小的类型(char, signed char, unsigned char, short, unsigned short等)首先要提升为int类型, 再执行运算. 根据原始类型进行位扩展(如果原始类型为unsigned char, 进行零扩展, 如果原始类型为signed char, 进行符号位扩展)到32位
signed char a = 0xe0; |
a为signed char, a在内存中的位储存形式是0xe0, 把a赋值给b, 所以b在内存中的位储存形式也是0xe0. 然后把a提升到int类型, 提升后会变成0xffffffe0(符号位扩展)
7. Type Size in 32-bit and 64-bit
32位和64位系统中字节数相同的类型:
- char: 1个字节
- short int: 2个字节
- int: 4个字节
- unsigned int: 4个字节
- float: 4个字节
- double: 8个字节
- long long: 8个字节
32位和64位系统中字节数不同的类型:
- pointer: 32位-4字节 64位-8字节
- long: 32位-4字节, 64位-8字节
- unsigned long: 32位-4字节, 64位-8字节
8. Private Destructor
为类对象分配栈空间时, 会先检查析构函数的访问性. 如果类的析构函数是private, 则编译器不会在栈空间上为类对象分配内存. 因此将析构函数设为私有, 类对象就无法建立在栈上(直接创建对象), 只能在堆上(new Class)分配类对象
class A { |
9. const reference
- 非const引用只能绑定到该引用同类型的对象
- const引用可绑定到不同但相关的对象
int a1 = 1; |
10. const and decltype
int x = 1; |
11. pointer of array
const char str1[] = "abc"; |
str1和str2都是数组指针, 存在常量区, 所以指针地址不同. p1和p2存在栈中, 虽然p1和p2的值不同, 但指向的都是同一块静态存储区.
12. constructor, destructor, and virtual function
对于constructor:
- constructor不能声明为virtual function: virtual function需在调用constructor时创建vtable来实现动态绑定; 若constructor为virtual function时, 调用constructor时没有vtable根据类对象类型调用, 因此无法通过编译.
- base class的constructor中不能调用virtual function: 当创建derived class的对象时, 若base class的constructor中使用virtual function, 由于derived class的构constructor的constructor还未执行完毕, 因此virtual function可能会操作还未初始化的成员.
class A {
public:
virtual void func() {
cout << "virtual A" << endl;
}
A() {
func(); // 调用A::func()
cout<<"A()"<<endl;
}
};
class B: public A {
public:
virtual void func() { cout << "virtual B" << endl; }
B() { cout << "B()" << endl; }
};
A *b = new B(); /* virtual A
* A()
* B()
*/
b->func(); /* virtual B */
对于destructor:
- base class的destructor中不能调用virtual function: destructor的执行顺序和constructor相反. C++会先销毁derived class, 再销毁base class. 当调用base class的virtual function时, 会先调用derived class的绑定函数, 但由于dervied class已被销毁, 因此会导致不可控结果
- base class的destructor应声明为virtual function: 当base class的destructor声明为virtual function时, 若指向base class的指针调用
delete, 会先销毁derived class, 再销毁base class. 当base class的destructor不为virtual function时, 若指向base class的指针调用delete, 只会销毁base class, 不会销毁derived class.
13. reference parameter
实参可以是任何类型(常量, 变量或表达式), 形参不能是表达式
void get1(char *p) { // p的地址并不与str相同, 但都指向NULL |
14. char*
char *s1; // s1未初始化, 所以地址不确定(野指针), 会导致错误 |
15. volatile
多线程中, 当多个线程修改和访问同一变量时, 会导致线程读取的变量可能已经被其他线程修改. 这主要是因为多线程中, 每个CPU会将变量装入CPU register中. 这样导致某个线程修改了变量后, 另一个线程由于没有去内存中同步变量, 而是直接从CPU register中读取, 从而使得线程不安全(因为从register直接读取会加快指令的执行速度).
volatile关键字让编译器取消优化, 每次读取变量都会从内存重新读取到CPU register中, 而不是使用register中的原来值, 从而使得线程安全.
16. Unary Operator
由于++和--有前缀和后缀两种形式, 后缀形式需添加一个int参数:
|
operator++(int)中的int是个哑元(dummy), 是永远用不上的, 它只是用来判断运算符是prefix还是postfix.
17. math.round
public static long round(double a); // 返回值为long |
math.round遵守四舍五入. 可以把int数值想象成数轴
< 0.5: 变为0, 趋向于原点>= 0.5: 变为1/-1, 远离原点
cout << round(0.4) << endl; // 10 |
18. scanf
space(空格), newline(换行)和tab(制表符)都可以用来分割(也可以是连续的空格, 换行或制表符). 逗号不能分割
19. Virtual method table
虚函数表的指针位置取决于编译器, C++标准中并没有明确规定. 但对于绝大多数编译器来说, 都会放在类的头部.
class Test { |
20. bool
C语言中没有bool类型, 可用int代替. C++才有bool类型
21. Preprocessor Directive
编译预处理与函数调用无关, 所在的位置决定作用域. main函数之后的预处理不会影响到main函数, main函数前定义的预处理会作用到main函数
|
上述代码中foo()函数没有影响a的值
|
上述代码中foo()函数在没有调用前就改变了a的值
22. constructor, copy constructor, and copy assignment operator
class A { |
23. Multiple Inheritance
class A { |
24. Pointer Arithmetic and array indexing
class A { |
第一个for循环的执行如下:
- 赋值: [0]a=1, [0]b=1, seta(): [0]a=2
- 赋值: [1]a=1, [1]b=1, seta(): [0]b=2
- 赋值: [2]a=1, [2]b=1, seta(): [1]a=2
- 赋值: [3]a=1, [3]b=1, seta(): [1]b=2
25. Heap Segment
long long a = 1, b = 2, c = 3; |
a, b, c各占8个字节, 但读取a,b,c时每个元素只读取四字节, 所以先读了a低字节的32位(1), b读取的是a的高字节32位(0), c读取的是b的低字节32位(2).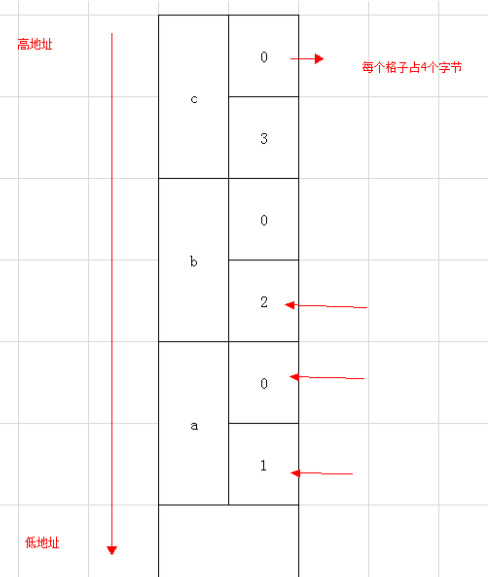
26. Operator Overloading
- 单目运算符最好重载为类的成员函数, 双目运算符则最好重载为类的友元函数
- =、()、[]、->、new、delete, 这些操作符必须为成员函数
27. strcat
strcat()要求第一个参数类型为char*, 且有足够的空间容纳两个字符串. 常量字符串虽然可以隐式转换为char*, 但字符串的内存大小固定, 无法扩充
char* p1 = "123", p2 = "456"; |
28. cast
- const_cast: 去除或添加指针或引用上的const或volatile关键字
const int *a = new int(1); // *a为1
int *b = const_cast<int*>(a); // 将const int*转换为int*
*b = 2; // *a为2 - static_cast: 执行一次显式类型转换, 可将基类指针转换为子类指针, 也可将enums转换为数值类型. 由于编译器会在运行static_cast时检查兼容性, 所以会保证类型转换是安全的
int a = 0x0001;
int* b = static_cast<int*>(a); // compile error - dynamic_cast: 只能用于多态中类的转换, 但不能用于钻石继承中的类转换, 或虚继承的类转换
class A{
virtual void func() {};
};
class B: public A {};
int main() {
A* aa = new A();
B* b = dynamic_cast<B*>(aa);
B* bb = new B();
A* a = dynamic_cast<A*>(bb);
} - reinterpret_cast
- 任意指针或引用类型之间的转换
- 指针与足够大的整数类型之间的转换
- 从整数类型(包括枚举类型)到指针类型的转换
29. strcmp return:
< 0: 第一个string小> 0: 第二个string小0: 两个string相等
30. static binding of default parameter
virtual function是动态绑定, 但缺省参数值是静态绑定
class A |