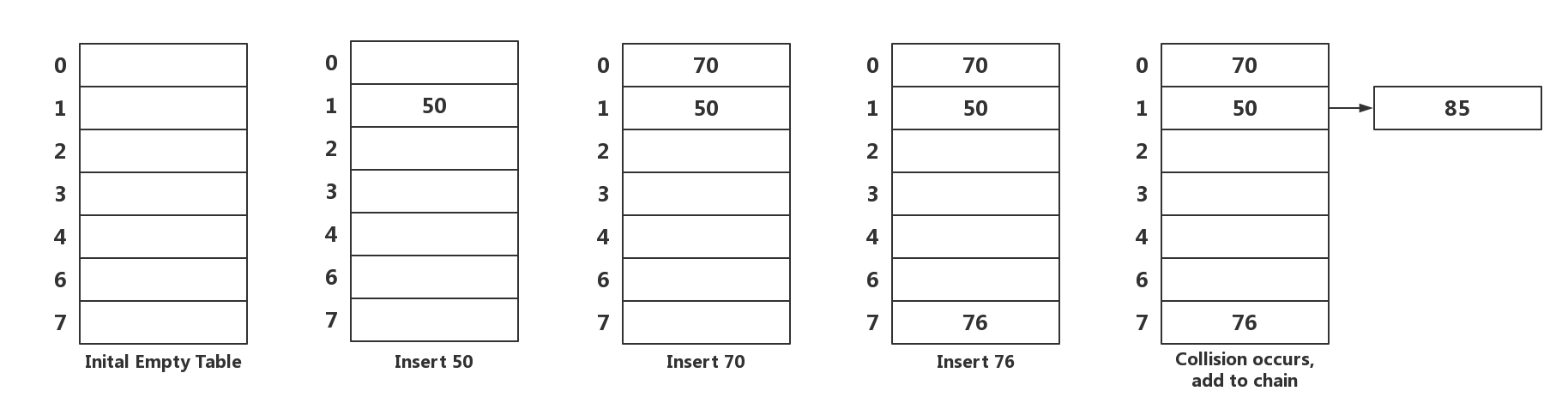
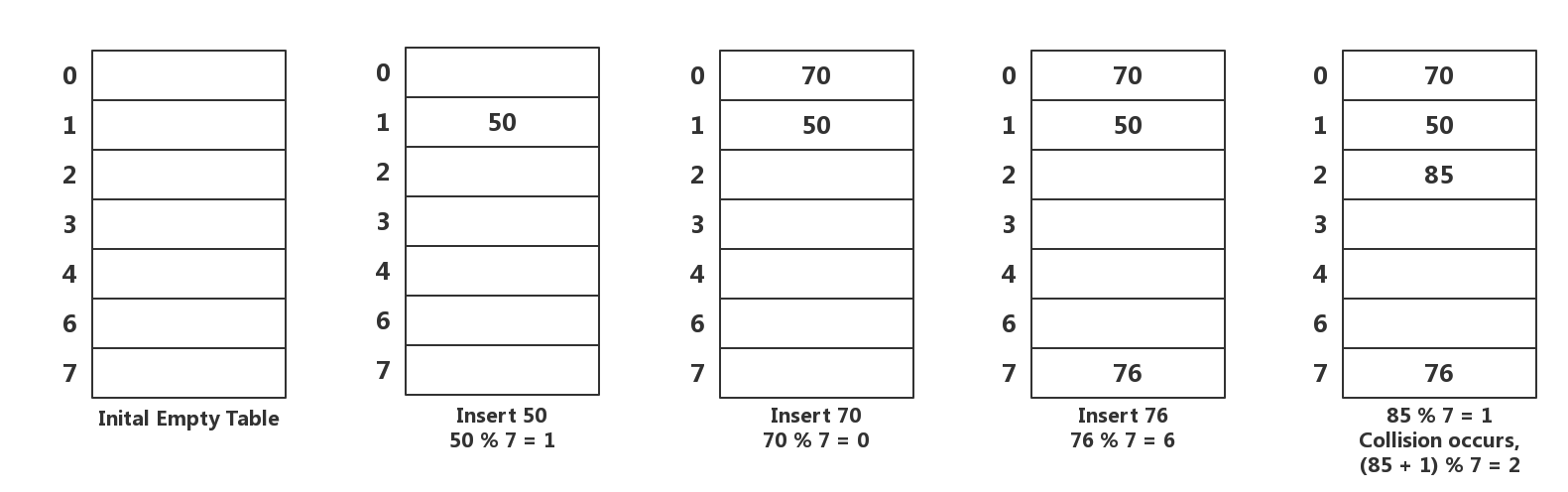
1. Hash Collision(哈希冲突) 当key的集合很大时, 根据Birthday Paradox(生日问题)原理, 哈希冲突是不可避免的. 所以必须采取一个哈希避免方法.
2 Hash Resolution 主流的解决方法有两种:
2.1 冲突链表法(Separate Chaining) 使用数组(假设数组名为table)保证读取效率为O(1), 使用hash function得到元素的hash value. hash value % table.length 表示元素在数组中的index. 如果index发生冲突, 该数组元素指向一个chain, chain中的元素拥有相同的index
2.2 开发地址法(Open addressing) 此方法将所有元素存在hash table中, 并不需要动态申请节点. 所以table的长度必须大于等于元素的个数.
插入元素: 如果hash function得出的hash value对应的slot不为空时, 继续进行probe, 直到找到一个空的slot.
查找元素: 不断probe直到元素为目标元素或slot为空.
删除元素: 由于查找元素时遇到slot为空则说明没有找到, 所以删除时不能将slot置为空, 只能标记该slot为"deleted"状态.
Open Addressing通过probe sequence(探测序列)来实现不断probing, 有以下几种探测序列:
Linear Probing(线性探测):
Quadratic Probing(二次探测):
double hashing probing(双重散列探测):
以Linear Probing为例, 现在有Hash value为50, 70, 76, 85
2.3 两种方式的优缺点对比
方式
Cache Performance
Space Wasting
need to know the number of elements
Search Performance
difficulty of implementation
demand of hash function
Separate Chaining
慢
多
不需要
慢
简单
低
Open Addressing
快
少
需要
快
较难
高
3. HashMap 3.1 HashMap结构 Java的HashMap采用了Separate Chaining作为Hash Collision的解决方法. 当table中某个slot所连的chain过长时, 将chain转化为Red-Black Tree, 用于提高搜索元素的效率.
已占用的slot数量 / 总slot数 >= load factor, 则需要对table进行扩容
已占用的slot数量 / 总slot数 < load factor, 则不需要对table进行扩容
假设table中有n个slot, 那么table的threshold会小于等于n, 这样装入table中的元素
3.2 重要参数 transient Node<K,V>[] table;int threshold;static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4 ; static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30 ;transient int modCount;transient int size;
3.3 table的组成单位 - Node static class Node <K,V> implements Map .Entry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; V value; Node<K,V> next; Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { this .hash = hash; this .key = key; this .value = value; this .next = next; } public final K getKey () { return key; } public final V getValue () { return value; } public final String toString () { return key + "=" + value; } public final int hashCode () { return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value); } public final V setValue (V newValue) { V oldValue = value; value = newValue; return oldValue; } public final boolean equals (Object o) { if (o == this ) return true ; if (o instanceof Map.Entry) { Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; if ( Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) && Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()) ) return true ; } return false ; } }
3.4 table扩容函数(也用于初始化) final Node<K,V>[] resize() { Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; int oldCap = (oldTab == null ) ? 0 : oldTab.length; int oldThr = threshold; int newCap, newThr = 0 ; if (oldCap > 0 ) { if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return oldTab; } else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1 ) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) newThr = oldThr << 1 ; } else if (oldThr > 0 ) newCap = oldThr; else { newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; newThr = (int )(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); } if (newThr == 0 ) { float ft = (float )newCap * loadFactor; newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float )MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? (int )ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); } threshold = newThr; @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node [newCap]; table = newTab; if (oldTab != null ) { for (int j = 0 ; j < oldCap; ++j) { Node<K,V> e; if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null ) { oldTab[j] = null ; if (e.next == null ) newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1 )] = e; else if (e instanceof TreeNode) ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this , newTab, j, oldCap); else { Node<K,V> loHead = null , loTail = null ; Node<K,V> hiHead = null , hiTail = null ; Node<K,V> next; do { next = e.next; if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0 ) { if (loTail == null ) loHead = e; else loTail.next = e; loTail = e; } else { if (hiTail == null ) hiHead = e; else hiTail.next = e; hiTail = e; } } while ((e = next) != null ); if (loTail != null ) { loTail.next = null ; newTab[j] = loHead; } if (hiTail != null ) { hiTail.next = null ; newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; } } } } } return newTab; }
4. HashMap初始化 4.1 默认的HashMap() static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f ;public HashMap () { this .loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; }
4.2 带参数的HashMap() static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30 ;public HashMap (int initialCapacity) { this (initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); } public HashMap (int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { if (initialCapacity < 0 ) throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); this .loadFactor = loadFactor; this .threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity); } static final int tableSizeFor (int cap) { int n = cap - 1 ; n |= n >>> 1 ; n |= n >>> 2 ; n |= n >>> 4 ; n |= n >>> 8 ; n |= n >>> 16 ; return (n < 0 ) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1 ; }
5. put() public V put (K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false , true ); } static final int hash (Object key) { int h; return (key == null ) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16 ); } final V putVal (int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 ) n = (tab = resize()).length; if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1 ) & hash]) == null ) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null ); else { Node<K,V> e; K k; if ( p.hash == hash && ( (k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)) ) ) e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this , tab, hash, key, value); else { for (int binCount = 0 ; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null ) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null ); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1 ) treeifyBin(tab, hash); break ; } if (e.hash == hash && ( (k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)) ) ) break ; p = e; } } if (e != null ) { V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null ) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null ; } Node<K,V> newNode (int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { return new Node <>(hash, key, value, next); }
6. get() public V get (Object key) { Node<K,V> e; return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value; } final Node<K,V> getNode (int hash, Object key) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1 ) & hash]) != null ) { if (first.hash == hash && ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return first; if ((e = first.next) != null ) { if (first instanceof TreeNode) return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); do { if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } while ((e = e.next) != null ); } } return null ; }
7. remove() public V remove (Object key) { Node<K,V> e; return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null , false , true )) == null ? null : e.value; } final Node<K,V> removeNode (int hash, Object key, Object value, boolean matchValue, boolean movable) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index; if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (p = tab[index = (n - 1 ) & hash]) != null ) { Node<K,V> node = null , e; K k; V v; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) node = p; else if ((e = p.next) != null ) { if (p instanceof TreeNode) node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key); else { do { if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) { node = e; break ; } p = e; } while ((e = e.next) != null ); } } if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value || (value != null && value.equals(v)))) { if (node instanceof TreeNode) ((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this , tab, movable); else if (node == p) tab[index] = node.next; else p.next = node.next; ++modCount; --size; afterNodeRemoval(node); return node; } } return null ; }