Hash Function
1. Introduction
Hash function用于将任意大小的数据映射为一个等长值, 理想的hash function遵循以下条件:
- 若两次输入相同, 则返回值相同
- 若两次输入不同, 则返回值不同
所有hash function一定满足第一个条件, 也就是说, hash function中不存在随机因素(deterministic); 但第二个条件理论上是无法满足: 输入为无穷集合, 输出为有限集合, 因此一定存在两个输入返回同一输出, 也称为collision(碰撞).
Hash function的返回值称为hash value(或简称为hash), 通常作为hash table的索引值(bucket index). 实现一个搜索key对应value的结构体可采用以下方式:
- unordered array:
$O(N)$ - BST:
$O(1.39\log(N))$ - Red-Black Tree:
$O(\log(N))$)
Hash table则可在常数时间内查找key对应的value.
1.1 Client vs. implementer
简单来说, hash function负责将key转换为bucket index, 这样就能将key类型的任意值保存到bucket中, 方便以后查找数据. Hash function可分为两部分:
- client提供的$h_\text{client}$函数: 将key转换为一个整数类型的hash code
- implementer提供的$h_\text{impl}$函数: 将hash code转换为一个bucket index
由于implementer只负责维护bucket, 并不了解key类型, 因此client负责将key类型的值转换为一个整数值(hash code); 由于client不了解implememter拥有多少bucket, 因此implementer负责将hash code转换为bucket index.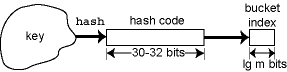
因此, hash function为$h_\text{client} \cdot h_\text{impl}$. 以Java为例, 通常Object的hash code为其内存地址, 若用hash code对bucket数量取模来获取bucket index, 由于内存地址通常是16的倍数, 因此只会使用到1/16的bucket.
1.2 Designing a hash function
一个hash function应具备以下属性:
- Injection: 若$k_1 \ne k_2$, 则$h(k_1) \ne h(k_2)$的概率应为$m-1/m$
- Diffusion: 若$k_1 \ne k_2$, 则$h(k_1)$不会提供$h(k_2)$的相关信息. 例如, $k_1$与$k_2$只差一个bit, 则$h(k_1)$的每个bit都有1/2的概率与$h(k_2)$不同.
我们可将hash function的设计拆为三个步骤:
- Serialization: 将key转换为包含key所有信息的byte stream(字节流). 以string为例, 其字节流为字符组成的字符串. 若$k_1 = k_2$, 则$h(k_1) = h(k_2)$.
- Diffusion: 将字节流转换为一个大整数x, 让字节流中的每个改动都能随机影响x的字节.
- 计算bucket index, 例如: $x\ mod\ m$
对于Serialization, 需保证key的所有信息都包含在字节流中, 以Java 1.1的hashCode()为例:
int hash = 0; |
虽然这种实现会加快字节流的计算过程, 但丢失了string的大量信息.
通常来说, client负责serialization和diffusion, hash table负责将hash code转换为bucket index. 有些hash table默认client生成的hash code十分随机, 因此直接将hash code的部分字节作为bucket index(hash table维持$2^n$的bucket个数); 另一些hash table额外执行一个integer hash function, 以提供更多diffusion, 因此client无需提供很好的hash code.
1.3 String Hashing
对于长度为l的字符串s, h(s)负责将s转换为[0, M]范围内的hash code, 则$h(s) = \sum^{l}_{i=1} s[i] \times b^{l-i}(\text{mod M})$, 例如, 对于字符串"xyz", 其hash code为$xb^2 + yb + z$.
该hash code计算方法可理解为: 将字符串s转换为一个b进制数. 假设字符串s与t发生哈希碰撞, 则$h(s) = h(t)$, 因此$\sum^{l}_{i=1}(s[i] - t[i])b^{l-i}(\text{mod M})$, 由于其在$\mathbb{Z}[x]$最多有l - 1个根, 若保证b从[0, M]之间均匀随机选取, 则可保证$h(s)$与$h(t)$的碰撞概率为$\frac{l-1}{M}$.
1.4 Collision Resolution
概率论中, birthday problem(生日问题)要求在一组随机选择的人群中, 找到至少有两个人生日相同(同月同日)的概率, 其结果是违背直觉的: 当人数达到23时, 至少两人生日相同的概率超过50%. 对于hash table, 这意味着若我们想要避免碰撞出现, 则bucket需要极大内存空间. 既然碰撞在所难免, 不如思考当碰撞发生时, 如何高效地处理该情况.
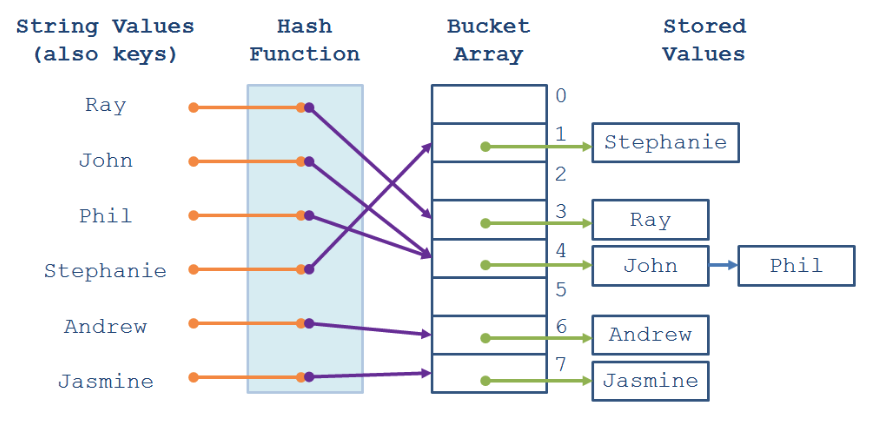
- Separate chaining: 将冲突的key放入与bucket index关联的链表中.
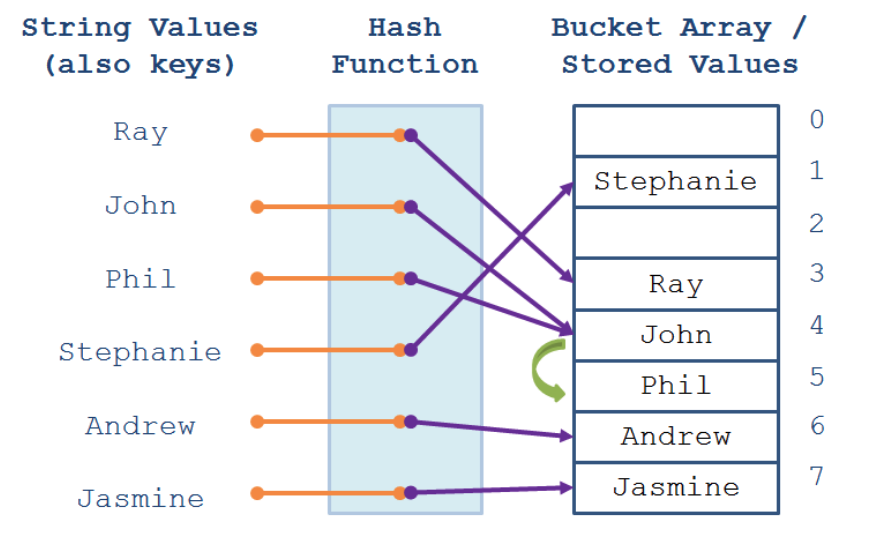
- Open addressing: 若key发生冲突, 则查询下一个空的bucket
假设向hash table中插入n个key-value pair, hash table中的bucket数为m:
- Separate chaining: 每个bucket的平均链表长度为
$\frac{n}{m}$. 若m过小, 则链表过长, 导致查询性能下降; 若m过大, 则有大量bucket不包含任何数据, 浪费内存, 因此一般保持$\frac{n}{m} \approx 10$. 当$\frac{n}{m} \gg 10$时, 则需重新计算所有key的hash value(无需新的hash code, 只需hash table计算新的bucket index), 以增大bucket数量. - Open addressing: 该方法有很多种探测下一个空bucket的算法, 上图为linear probing. Linear probing运行时会出现一段连续使用的bucket, 称为clustering, 导致插入key时, 该key落在clustering之后bucket的概率比其他bucket大, 因此clustering的长度决定了hash table的插入和查询速度. 假设
$\alpha = \frac{n}{m}$, 则查询指定key所需的平均操作数为$\frac{1}{2}(1+\frac{1}{(1-\alpha)})$, 插入指定key所需的平均操作数为$\frac{1}{2}(1+\frac{1}{(1-\alpha)^2})$, 若保持$\frac{n}{m} = \frac{1}{2}$, 则查询需访问$\frac{3}{2}$个bucket, 插入需访问$\frac{5}{2}$个bucket. 若$\frac{n}{m} \gg \frac{1}{2}$, 与separate chaining相同, 仍需重新计算所有key的hash value, 以增大bucket数量.
2. Rolling Hash
对于在长度为N的字符串a中查找长度为M的字符串b(通常$N \gg M$)问题, 目前存在四种主流方法:
- Brute Force
- KMP
- Boyer-Moore
- Rabin-Karp
其中Rabin-Karp采用一种rolling hash的方式计算字符串a中每个长度为M的子字符串的hash value, 并对比字符串b的hash value, 算法步骤如下:
- 计算字符串b的hash value, 记为
$h_b$ - 遍历a中每一个坐标
i, 计算$a[i, i+M-1]$的hash value, 记为$h_{pat}$ - 对比
$h_b$与$h_{pat}$是否相等
采用modular hash function计算字符串的hash value时, 若字符串a中第i个字符为$t_i$, 则以$t_i$为起点, 长度为M的字符串的hash value $x_i$为$t_{i}R^{M-1} + t_{i-1}R^{M-2} + \ldots + t_{i+M-1}R^0 \text{ (mod Q)}$, 而$x_{i+1} = t_{i+1} R^{M-1} + t_i R^{M-2} + \ldots + t_{i+M} R^0$, 若已知$x_i$, 则可直接计算$x_{i+1}$: $x_{i+1} = (x_{i} - t_{i}R^{M-1})R + t_{i+M}$.
3. Bloom Filter
假设hash set的数组长度为q, 已插入n个元素, 若使用separate chaining解决collision, 则每个数组元素的链表约为$\frac{n}{q}$, 称为$\alpha$, 因此hash set添加或查找元素的时间复杂度为$O(1+\alpha)$, 其空间复杂度为O(mn), 其中m为元素所占bit数. 假设在hash set中存放10亿个整数, 则至少需要40亿字节, 也就是4TB内存; 若存放网页URL, 由于单个URL所占字节数远超单个整数, 会需要更大的内存空间.
可以发现, hash set为了解决collision, 需在hash set中保留每个元素副本; 但若业务允许一定的失误率, 则可以大幅减少内存需求, 如bloom filter.
Bloom filter需创建一个长度为q的bit array, 全部初始化为0, 并创建k个hash function($k_1, k_2, \ldots, h_k$), 这些hash function产生的hash value位于[0, q-1]区间:
- 插入元素时: 每个hash function产生一个hash value, 并将bit array坐标对应值置为1
- 查找元素时: 每个hash function产生一个hash value:
- 若bit array中所有坐标对应值均为1, 则元素极大概率存在
- 若bit array中其中一个坐标对应值为0, 则元素一定不存在
若bloom filter中存放10亿个整数, 则需10亿bit的内存空间, 也就是125GB; 若元素类型改为字符串, 内存需求仍不变: bloom filter的内存需求只与元素个数有关, 与元素类型无关. 但代价是error rate: bloom filter的错误率只与q和k有关.
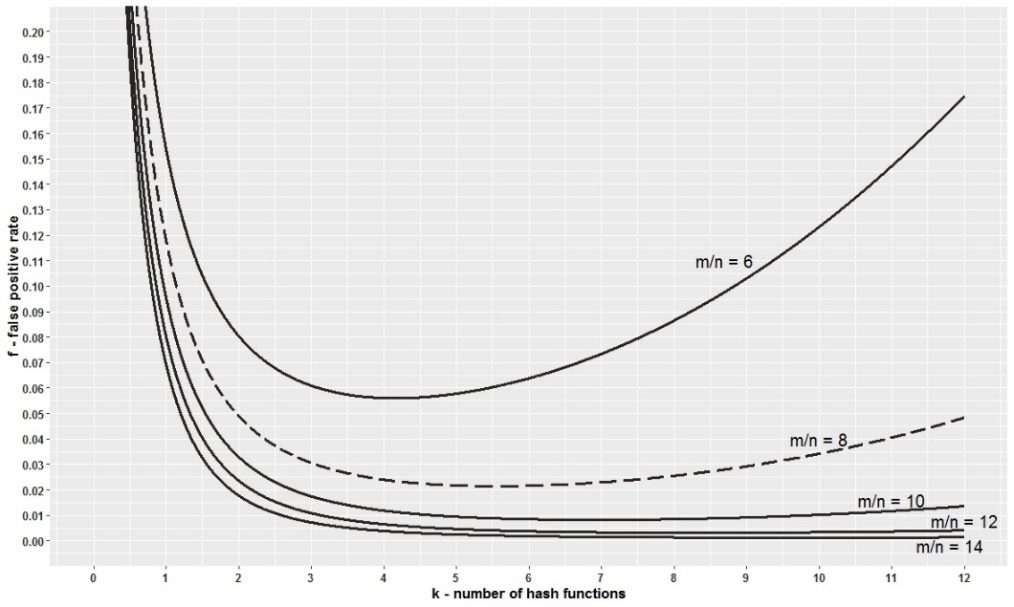
上图中, 横轴为hash function的数量(k), 纵轴为error rate(f, 元素实际不存在, 但误报存在的概率), 多条曲线表示元素数量(n)确定的情况下, bit array长度(m)对error rate的影响. 可以发现:
- m越大, 失误率越低
- p呈现抛物线, 因此, 在m和n确定的情况下, 可计算出最佳p值
设计bloom filter时, 先根据失误率f(业务可接受的最高失误率)和元素数量n(业务中的元素数量上限)确定bit array长度m, 再根据m和n确定hash function数量p.
187. Repeated DNA Sequences
The DNA sequence is composed of a series of nucleotides abbreviated as 'A', 'C', 'G', and 'T'.
- For example,
"ACGAATTCCG"is a DNA sequence.
When studying DNA, it is useful to identify repeated sequences within the DNA.
Given a string s that represents a DNA sequence, return all the 10-letter-long sequences (substrings) that occur more than once in a DNA molecule. You may return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
Input: s = "AAAAACCCCCAAAAACCCCCCAAAAAGGGTTT" |
Example 2:
Input: s = "AAAAAAAAAAAAA" |
Rolling Hash + Double Hashing
计算字符串内所有长度为10的子字符串的hash value, 若存在相同hash value, 则认为DNA序列重复, 需注意以下几点:
- 重复的DNA序列只添加一次, 因此需hashset过滤
- 若输入字符串过长, 则容易发生collision, 因此采用double hashing
class Solution { |
718. Maximum Length of Repeated Subarray
Given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, return the maximum length of a subarray that appears in both arrays.
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [1,2,3,2,1], nums2 = [3,2,1,4,7] |
Binary Search + Rolling Hash
若nums1和nums2存在一个长度为k的公共子数组, 则一定存在长度为$j <= k$的公共子数组, 因此可使用binary search查找最大k. 最长公共子数组的长度范围为[0, min(|nums1|, |nums2|)], 取长度m, 分为两种情况:
- 无法找到长度为m的公共子数组: 继续查找
[0, m-1]范围 - 找到长度为m的公共子数组: 查找查找
[m+1, min(|nums1|, |nums2|)]范围
lass Solution { |
214. Shortest Palindrome
You are given a string s. You can convert s to a palindrome by adding characters in front of it.
Return the shortest palindrome you can find by performing this transformation.
Example 1:
Input: s = "aacecaaa" |
Example 2:
Input: s = "abcd" |
Rolling Hash
题目要求在字符串s前添加最短字符串$s'$, 使得$s+s'$成为回文字符串. 假设s的长度为n, 最差情况时, $s'$的长度为n-1(s第一个字符之后的其他字符), 因此$|s'| < |s|$. 由于$s + s'$是一个回文字符串, 因此s可分为两部分:
- s1: 自身为一个回文字符串
- s2: 与$s'$互为回文
若想要$s'$最短, 则需找到最长s1, 因此题目可替换为: 如何在s中找到以0坐标为起点的最长回文字符串: 若子字符串的正序hash value与反序hash value相等, 则说明该子字符串为回文字符串.
class Solution { |
1044. Longest Duplicate Substring
Given a string s, consider all duplicated substrings: (contiguous) substrings of s that occur 2 or more times. The occurrences may overlap.
Return any duplicated substring that has the longest possible length. If s does not have a duplicated substring, the answer is "".
Example 1:
Input: s = "banana" |
Binary Search + Rolling Hash
假设字符串s的长度为n, 则重复的子字符串的长度范围为[0, n-1], 若存在长度为L的重复子字符串, 则一定存在长度为L-1的重复子字符串, 因此可使用binary search查找最长重复子字符串.
计算s中每个长度为L的子字符串的hash value, 若存在相同hash value, 则说明存在重复的子字符串, 因此使用rolling hash计算.
需要注意的是, 若s过长, 会出现collision, 可使用double hash避免collision.
class Solution { |
1316. Distinct Echo Substrings
Return the number of distinct non-empty substrings of text that can be written as the concatenation of some string with itself (i.e. it can be written as a + a where a is some string).
Example 1:
Input: text = "abcabcabc" |
Example 2:
Input: text = "leetcodeleetcode" |
Presum + Rolling Hash
题目要求找到所有a + a模式的子字符串, 假设子字符串s符合规则, 则s的长度必为偶数, 由字符串s1和s2组成, 且s1 = s2. 由于s1(或s2)的长度范围为$(2, 4, 6, 8, \ldots, \frac{|s|}{2})$, 因此可遍历所有可能长度, 并比较s1和s2是否相同. 实现时需注意以下几点:
- 题目要求不同的子字符串, 因此需要hash set去重
- 若将
[a, z]映射为[0, 25], 会导致a与aa的hash value同为0, 因此可映射为[1, 26] - 每个长度都需对字符串执行一遍rolling hash, 该过程可使用presum加速: 假设
h[i:j]表示text[i:j]的hash value, 可遍历text并使用rolling hash计算所有前缀和h[0,i], 当需要获得某段子字符串的hash value时, 可执行$h[i:j] = h[0,j] - h[0,i-1] * K^{j-i}$.
class Solution { |
1147. Longest Chunked Palindrome Decomposition
You are given a string text. You should split it to k substrings $(\text{subtext}_1, \text{subtext}_2, \ldots, \text{subtext}_k)$ such that:
$\text{subtext}_i$is a non-empty string.- The concatenation of all the substrings is equal to
text(i.e.,$\text{subtext}_1 + \text{subtext}_2 + \ldots + \text{subtext}_k == \text{text}$). $\text{subtext}_i == \text{subtext}_{k-i+1}$for all valid values ofi(i.e.,$1 \le i \le k$).
Return the largest possible value of k.
Example 1:
Input: text = "ghiabcdefhelloadamhelloabcdefghi" |
Example 2:
Input: text = "merchant" |
Greedy + Two Pointers + Rolling Hash
题目要求返回subtext的最大数量, 因此应保证每段subtext尽量短. 对于subtext[i]和subtext[k-i+1], 存在以下情况:
- 若
subtext[i] == subtext[k-i+1]: k += 2 - 若
i < k-i+1且subtext[i] != subtext[k-i+1]: i++ - 若
i >= k-i+1: 存在以下两种可能:- 未找到互为镜像的subtext, 如
AXA,X不存在镜像, k++ text不存在单独的subtext, 如ABBA, k不变
- 未找到互为镜像的subtext, 如
判断subtext[i]和subtext[k-i+1]是否相同可通过rolling hash实现.
class Solution { |
1923. Longest Common Subpath
There is a country of n cities numbered from 0 to n - 1. In this country, there is a road connecting every pair of cities.
There are m friends numbered from 0 to m - 1 who are traveling through the country. Each one of them will take a path consisting of some cities. Each path is represented by an integer array that contains the visited cities in order. The path may contain a city more than once, but the same city will not be listed consecutively.
Given an integer n and a 2D integer array paths where paths[i] is an integer array representing the path of the $i^{th}$ friend, return the length of the longest common subpath that is shared by every friend's path, or 0 if there is no common subpath at all.
A subpath of a path is a contiguous sequence of cities within that path.
Example 1:
Input: n = 5, paths = $[[0,1,\underline{2,3},4]$, |
Example 2:
Input: n = 3, paths = [[0],[1],[2]] |
Binary Search + Rolling Hash + Double Hash
假设m个数组中, 最长公共子数组的长度为len, 则:
- 一定存在长度为
$\text{len}' \le \text{len}$的公共子数组 - 一定不存在长度为
$\text{len}' \gt \text{len}$的公共子数组
因此可使用binary search查找len, 上限为m个数组的最短数组长度, 下限为1. 对于任意长度n, 需判断是否所有数组都存在长度为n的公共子数组, 因此可使用rolling hash计算每个数组中长度为n的子数组的hash value, 并判断是否全部数组都包含该hash value.
class Solution { |