Priority Queue
1. Introduction
开发程序时经常需要对数据进行排序, 但有时无需排序所有数据, 例如: 先排序一部分数据, 处理第一位的元素后, 接收更多数据, 再处理当前数据的第一位元素. 对于移除最大(小)值并插入数据的操作, 可使用名为Priority Queue的数据结构. Priority Queue(优先队列, 缩写为pq)需实现以下操作:
add(DataType item, int pri): 向pq添加元素,item为元素本身,pri为元素的优先级DataType peek(): 查看最高(低)优先级的元素DataType remove(): 移除并返回最高(低)优先级的元素
以下是几种实现Priority Queue的方式:
- 基于Ordered Array的PQ:
add(): 使用binary search找到新元素插入的位置, 并将其后的元素向后移动一格, $O(\log(N)) + O(N) = O(N)$peek(): 返回array的最后一个元素, $O(1)$remove(): 移除array的最后一个元素, $O(1)$
- 基于Unordered Array的PQ:
add(): 将元素放在数组尾部, $O(1)$peek(): 扫描整个数组, 并返回最大(小)优先级的元素, $O(N)$remove(): 扫描整个数组, 找到最大(小)优先级的元素, 并将之后元素向前移动一格, $O(N)$
- 基于Ordered LinkedList的PQ:
add(): 扫描整个链表并将其放入合适的位置, $O(N)$peek(): 返回链表首位, $O(1)$remove(): 返回链表首位, $O(1)$
- 基于Unordered LinkedList的PQ:
add(): 将元素加入链表头部, $O(1)$peek(): 需扫描整个链表, $O(N)$remove(): 需扫描整个链表, $O(N)$
- 基于Binary Search Tree的PQ: 假设tree保持平衡
add(): $O(log(N))$peek(): $O(log(N))$remove(): $O(log(N))$
以下是各种实现的对比:
| Sorted Array | Unordered Array | Ordered Linked List | Unordered Linked List | Binary Search Tree | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
add() |
$O(N)$ | $O(1)$ | $O(N)$ | $O(1)$ | $O(log(n))$ |
peek() |
$O(1)$ | $O(N)$ | $O(1)$ | $O(N)$ | $O(log(n))$ |
remove() |
$O(1)$ | $O(N)$ | $O(1)$ | $O(N)$ | $O(log(n))$ |
2. Binary Heap
Binary Heap是一种binary tree, 且拥有以下属性:
- 是一个complete tree(只有最下面两层节点的child数小于2,且最下面一层的节点都集中在最左边的连续位置上)
- Parent node的优先级大于等于(或小于等于)其两个child node
以下是一个binary heap: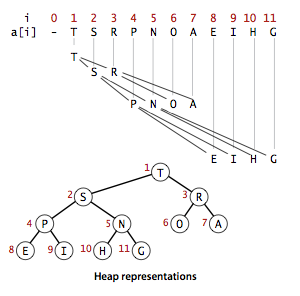
可以发现, binary heap可用一个数组表示: 假设root node从1开始, root的child node分别在2和3坐标, 可推断出: 若节点的坐标为i, 则其parent node的坐标为k/2, left child的坐标为2k, right child的坐标为2k+1. 但数组中任意数据的修改都会破坏binary heap的属性, 因此需要一些方法来维护binary heap的属性(假设heap遵循$\text{priority of parent node} \ge \text{priority of child node}$):
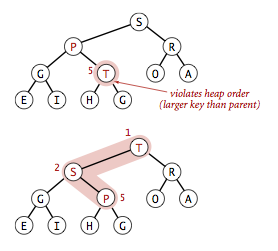
- Bottom-up heapify: 若当前节点的优先级大于其父节点的优先级, 则其违背了binary heap的特性, 因此可让当前节点与父节点交换; 若交换后, 父节点的优先级大于与其父节点的优先级, 则继续交换, 直到满足优先级规则, 或节点变为root.
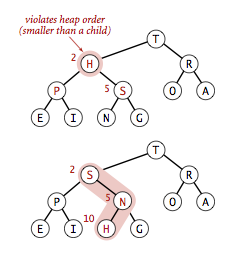
- Top-down heapify: 若当前节点的优先级小于其中一个或两个子节点, 则与优先级最大的子节点交换, 并以此类推, 直到其满足优先级规则, 或没有任何子节点.
因此, 可使用binary heap实现priority queue:
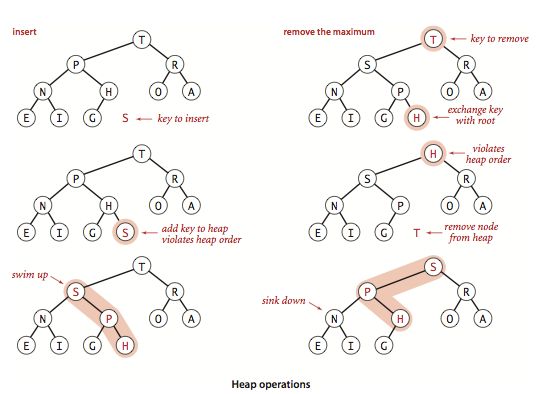
add(): 数组尾部追加元素, 并对该元素使用bottom-up heapify以保持binary heap属性peek(): 取出数组头部的元素remove(): 将数组头部元素与尾部交换, 并对头部元素使用top-down heapify以保持binary heap属性
基于binary heap的priority queue的时间复杂度如下:
add(): $O(\log(N))$peek(): $O(1)$remove(): $O(\log(N))$
862. Shortest Subarray with Sum at Least K
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return the length of the shortest non-empty subarray of nums with a sum of at least k. If there is no such subarray, return -1.
A subarray is a contiguous part of an array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,-1,2], k = 3 |
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2], k = 4 |
Greedy + Priority Queue
若计算数组的前缀和presum, 则问题转变为: 如何在presum中找到两个坐标i, j, 满足presum[j] - presum[i] >= k. 因此可使用priority queue和贪心算法, 将前缀和和坐标保存在pq中, 若presum[i]与pq头部元素(最小前缀和)的差值大于k, 则弹出pq头部元素, 当前坐标与该元素构成一个subarray:
- 若
pq的下一个头部元素满足条件, 则继续弹出; 若头部不满足条件, 则pq剩下元素必定不满足 - 即使之后坐标与
pq头部元素也满足条件, 但会长于当前坐标组成的subarray, 因此无需考虑
class Solution { |
295. Find Median from Data Stream
The median is the middle value in an ordered integer list. If the size of the list is even, there is no middle value, and the median is the mean of the two middle values.
- For example, for
arr = [2,3,4], the median is3. - For example, for
arr = [2,3], the median is(2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5.
Implement the MedianFinder class:
MedianFinder()initializes theMedianFinderobject.void addNum(int num)adds the integernumfrom the data stream to the data structure.double findMedian()returns the median of all elements so far. Answers within$10^{-5}$of the actual answer will be accepted.
Example 1:
Input |
Priority Qyeye
假设一个排序好的数组为$[{num}_1, {num}_2, \cdots, {num}_{2n-1}, {num}_{2n}]$, 其中${num}_i \le {num}_{i+1}$, 该数组可拆分为两个数组: $[{num}_1, {num}_2, \cdots, {num}_{n-1}, {num}_n]$和$[{num}_{n+1}, {num}_{n+2}, \cdots, {num}_{2n-1}, {num}_{2n}]$, 可以看做一个max heap, 一个min heap, 因此中位数为$(max-heap.peek() + min_heap.peek()) / 2; 若数组中元素数为奇数, 则max heap或min heap的头部元素为中位数.
class MedianFinder { |
480. Sliding Window Median
The median is the middle value in an ordered integer list. If the size of the list is even, there is no middle value. So the median is the mean of the two middle values.
- For examples, if
arr = [2,3,4], the median is3. - For examples, if
arr = [1,2,3,4], the median is(2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5.
You are given an integer array nums and an integer k. There is a sliding window of size k which is moving from the very left of the array to the very right. You can only see the k numbers in the window. Each time the sliding window moves right by one position.
Return the median array for each window in the original array. Answers within $10^{-5}$ of the actual value will be accepted.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], k = 3 |
Slide Window + Priority Queue
乍看之下该题目与上一题相同, 都是求一段连续序列的中位数, 但由于是滑动窗口, 因此必须将最左端的元素弹出priority queue, 且无法判断该元素存在于max heap还是min heap, 因此需要priority queue具有删除特定元素的功能. 由于Java的PriorityQueue不支持, 因此可以自己实现: IndexPriorityQueue添加元素时需提供两个参数: key和value, key表示元素的唯一标识(数组坐标), value表示元素的优先级(元素数值). 按照以下步骤删除元素:
- 通过key找到对应元素在binary heap中的位置
- 将该元素与binary heap的数组尾部元素调换
- 对当前位置的元素调用bottom-up heapify和top-down heapify
class Solution { |
218. The Skyline Problem
A city's skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that city when viewed from a distance. Given the locations and heights of all the buildings, return the skyline formed by these buildings collectively.
The geometric information of each building is given in the array buildings where $\text{buildings}[i] = [\text{left}_i, \text{right}_i, \text{height}_i]$:
$\text{left}_i$is the x coordinate of the left edge of the$i^{th}$building.$\text{right}_i$is the x coordinate of the right edge of the$i^{th}$building.$\text{height}_i$is the height of the$i^{th}$building.
You may assume all buildings are perfect rectangles grounded on an absolutely flat surface at height 0.
The skyline should be represented as a list of "key points" sorted by their x-coordinate in the form $[[x_1,y_1],[x_2,y_2],...]$. Each key point is the left endpoint of some horizontal segment in the skyline except the last point in the list, which always has a y-coordinate 0 and is used to mark the skyline's termination where the rightmost building ends. Any ground between the leftmost and rightmost buildings should be part of the skyline's contour.
Note: There must be no consecutive horizontal lines of equal height in the output skyline. For instance, [...,[2 3],[4 5],[7 5],[11 5],[12 7],...] is not acceptable; the three lines of height 5 should be merged into one in the final output as such: [...,[2 3],[4 5],[12 7],...]
Example 1:
Input: buildings = [[2,9,10],[3,7,15],[5,12,12],[15,20,10],[19,24,8]] |
Line Sweep + Priority Queue
由于key point只会出现在建筑的left edge或right edge上, 因此可从左向右扫描所有edge. 将所有建筑的left edge和right edge按照x坐标从小到大排序, 对于任意x坐标(与y轴平行的线), 存在两种可能:
- 不存在重叠建筑: 该edge一定存在key point
- 存在重叠建筑: 该edge不一定存在key point, 因此edge对应的建筑可能被更高的建筑遮盖
为判断x坐标上的建筑是否存在重叠, 可对每个横坐标检查一遍所有建筑, 并找出最高的建筑, 判断该建筑之前是否已添加到结果中; 但这么时间复杂度变为$O(N^2)$, 可使用priority queue优化寻找最大高度的问题, 对于任意x坐标$x_i$:
- 若存在建筑的$\text{left edge} \le x_i$, 则将建筑的right edge放入
pq - 若
pq头部元素的$\text{right edge} \ge x_i$, 则将pq的头部元素弹出 pq的头部元素一定为$x_i$之前的最高建筑, 存在两种可能:- 该建筑在$x_i$上存在left edge或right edge: 存在key point
- 该建筑在$x_i$上不存在left edge或right edge: 不存在key point
class Solution { |