ConfigMap and Secret
1. Introduction
配置信息的存储是所有应用开发都无法回避的一个环节, 在K8s还未推广的日子里, 被放入container的应用代码有以下几种方式获取其配置信息:
- 将配置信息放置在某个文件中, 该文件称为config file(配置文件): 在image中写入密钥等配置信息, 所有可以访问image的人都可以获取密钥
- 在environment variable(环境变量)中添加配置信息:
docker run -e “password=abc” - 使用docker secret: 必须在Docker Compose中使用,
- 将配置文件以volume的形式挂载在container的某个目录上
2. Pass Command-line Arguments to Containers
K8s可以向pod中的container传递一个自定义命令行参数, 以下是两种实现方式:
2.1 Define the Command and Arguments in Docker
Dockerfile中提供了两个instructions(指令):
- ENTRYPOINT: 指定container启动时运行的command, 不可被
docker run的参数覆盖 - CMD: 若dockerfile中未定义ENTRYPOINT, 则作为container启动时运行的command; 否则为ENTRYPOINT提供参数. 可被
docker run的参数覆盖
总结一下, Dockerfile中存在三种情况:
- 只定义CMD: container启动时执行CMD中的命令,
docker run的参数会替代CMD的参数 - 只定义ENTRYPOINT: container启动时执行ENTRYOPOINT的命令,
docker run的参数会附加到ENTRYPOINT上 - 包含ENTRYPOINT和CMD: container启动时执行ENTRYPOINT的命令, 并将CMD的参数附加到ENTRYPOINT上,
docker run的参数会替代CMD
因此, 通常将container执行的命令放在ENTRYPOINT中, 将默认参数放在CMD中, docker run的参数用于重载CMD的参数.
ENTRYPOINT和CMD执行命令时存在两种形式:
- exec:
ENTRYPOINT ["executable", "arg1", "arg2"] - shell:
ENTRYPOINT command arg1 arg2
exec和shell的区别如下:
- exec直接执行可执行文件, 无需调用shell; shell在shell中执行命令, 如
/bin/sh -c - 由于shell不会将收到signal发给其子进程, 当shell收到
SIGTERM时, exec执行的进程不会收到任何信号; shell执行的程序可捕捉到该信号并进行处理 - 由于exec不在shell中执行, 因此exec中的程序无法获取shell的环境变量, 如
$HOME; shell执行的程序可继承shell的所有环境变量
因此, 通常ENTRYPOINT和CMD使用exec形式, RUN使用shell形式.
2.2 Override the Command and Arguments in Kubernetes
K8s可重写contianer的ENTRYPOINT和CMD:
... |
| Docker | Kubernetes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ENTRYPOINT | command | The executable that's executed inside the container |
| CMD | args | The arguments passed to the executable |
通常不需要重写ENTRYPOINT, 除了一些不包含ENTRYPOINT的image, 如busybox.
需要注意的是, args中的数字必须用double quote(双引号)包裹, 字符串则不必.
3. Set Environment Variables for a Container
K8s可为pod中的每个container分配各自的environment variables, 但k8s不支持在pod层面上设置并让所有container共享environment variable: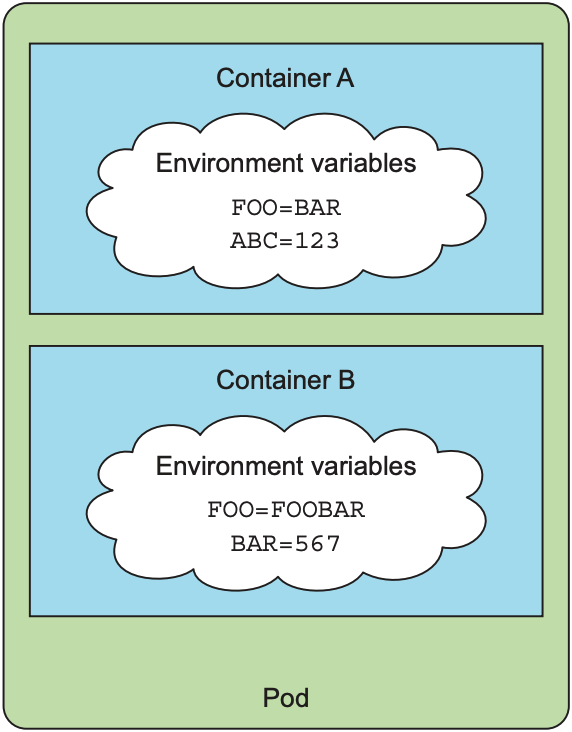
... |
K8s还支持在YAML中使用已设置的变量(包括环境变量): 使用$(VAR)即可调用之前定义的变量:
... |
上述例子中, FIRST_VAR为foo, SECOND_VAR为foobar. 将配置信息放置在环境变量会导致一个问题: 不同环境(dev或prod)需要不同的pod定义文件. 因此需要将配置信息与pod定义分离, k8s提供了两种方式:
- ConfigMap: 用于存储配置信息
- Secret: 用于存储敏感信息
4. ConfigMap
ConfigMap作为K8s的resource之一, 其目的是将配置信息从程序代码, 部署更新, 和运行环境中分离出来. ConfigMap可看作一个map, 其中包含一个或多个键值对(key/value pair). Container中运行的程序不会直接读取ConfigMap中的键值对, 而是通过environment variables或volume的形式将配置信息加载到container上: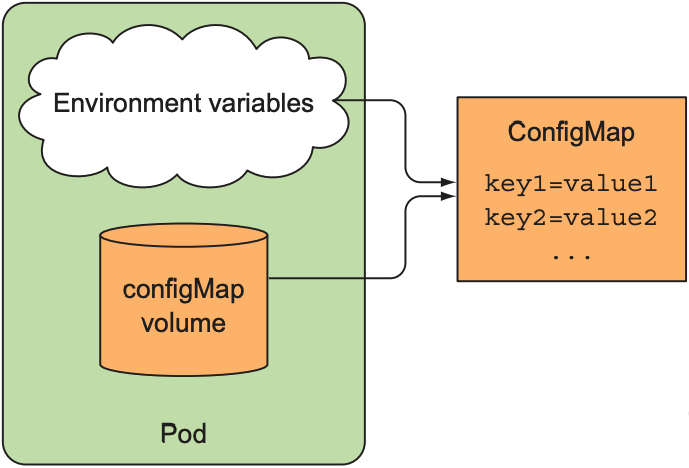
ConfigMap不与pod绑定, 只与namespace绑定, 因此:
- 同一namespace下的pod共享所有ConfigMap
- 不同namespace下的ConfigMap可拥有相同name
4.1 Create a ConfigMap
两种方式创建ConfigMap:
- 使用kubectl命令:
kubectl create configmap - 使用YAML文件:
kubectl create -f
$ kubectl create configmap fortune-config --from-literal=sleep-interval=25 |
上述指令创造了一个名为fortune-config的ConfigMap, 包含一个键值对, key为sleep-interval, value为25. 也可在一个ConfigMap中创建多个键值对:
$ kubectl create configmap myconfigmap --from-literal=foo=bar \ |
执行kubectl get configmap命令可查看当前ConfigMap
$ kubectl get configmap fortune-config -o yaml |
--from-literal后跟键值对. --from-file后跟文件名或文件目录, 例如:
$ kubectl create configmap my-config --from-file=config-file.conf |
上述新建的ConfigMap名为my-config, 包含一个键值对, key为文件名(config-file.conf), value为该文件的内容.
$ kubectl create configmap my-config --from-file=/path/to/dir |
指定目录下的文件都会作为键值对放入ConfigMap中. ConfigMap也支持混合使用上述几种方式, 如下:
$ kubectl create configmap my-config \ |
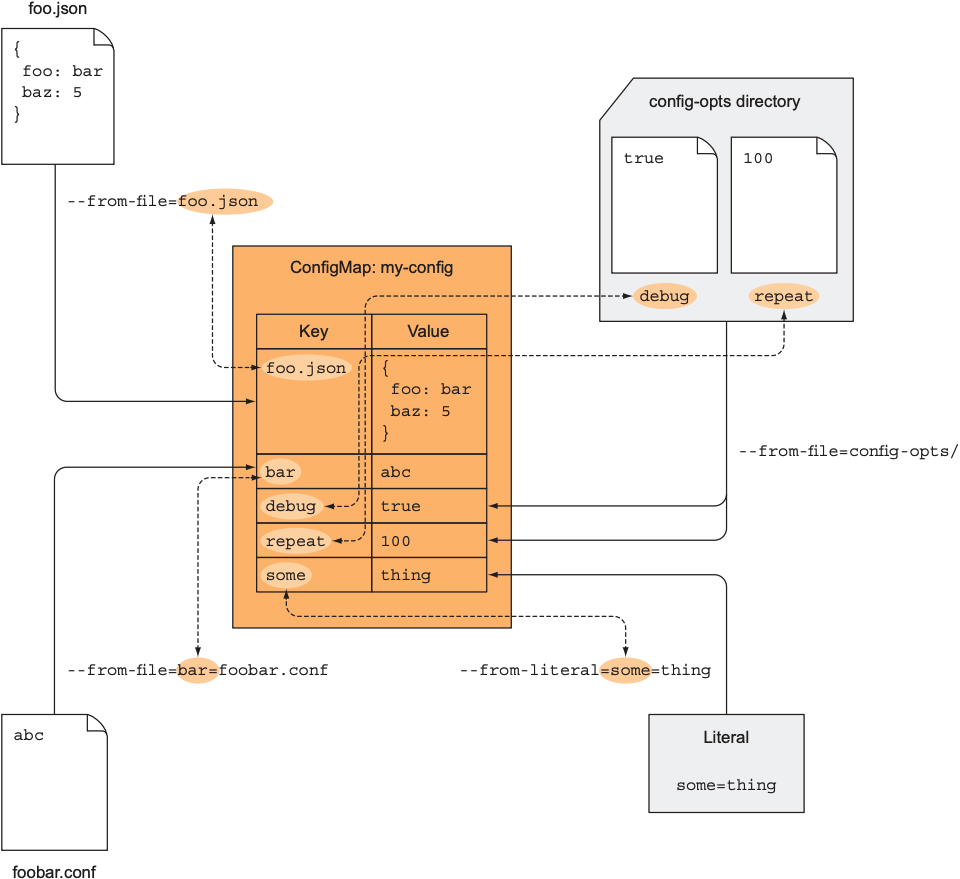
4.2 Pass a ConfigMap Entry to a Container as an Environment Variable
K8s支持将ConfigMap的键值对以环境变量的形式导入到pod的container中:
apiVersion: v1 |
上述例子中, container中设置了一个环境变量, 其key为INTERVAL, value为ConfigMap(fortune-config)中key(sleep-interval)对应的value值. 若ConfigMap不存在, 则不会启动该container, 且依旧运行pod的其他container; 创建缺失的ConfigMap会自动启动该container. 若设置configMapKeyRef.optional: true, 则即使ConfigMap不存在也会启动container.
4.3 Pass all Entries of a ConfigMap as Environment Variable
K8s 1.6提供了一种将ConfigMap中的所有键值对导入环境变量的方法:
spec: |
上述所有环境变量都以CONFIG_开始. 需要注意的是, 环境变量不支持一些特殊符号. 若ConfigMap中的key或value包含不合规符号(如foo-bar), 则该键值对不会导入环境变量.
4.4 Pass a ConfigMap Entry as a Command-line Argument
ConfigMap中的键值对也可借助环境变量作为命令行参数传入container:
apiVersion: v1 |
结果如下图: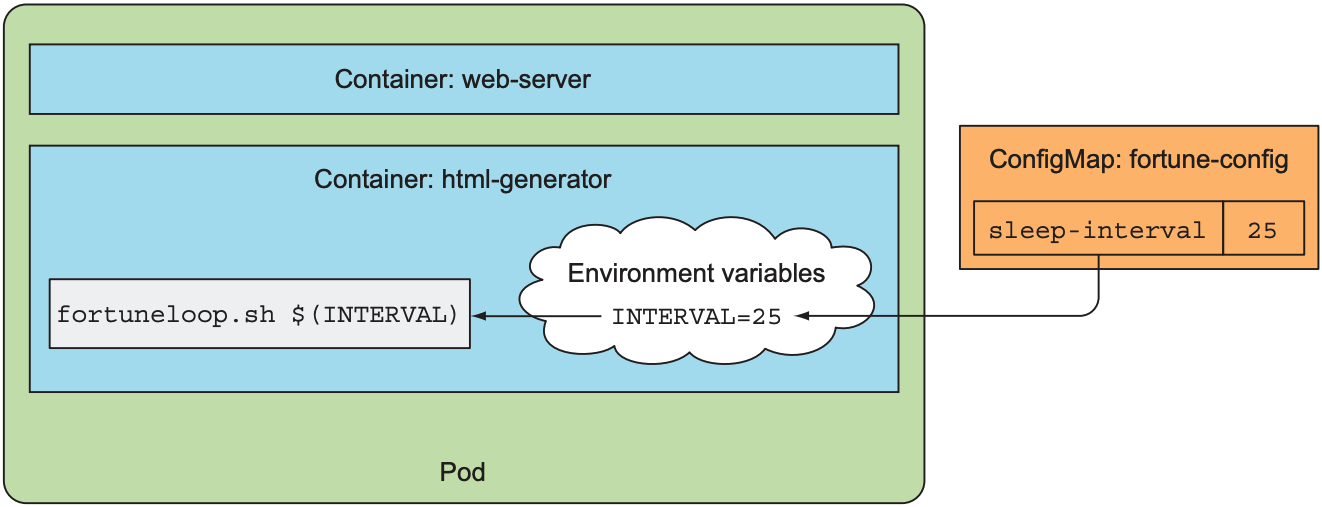
4.5 Use a ConfigMap Volume to Expose ConfigMap Entries as Files
将ConfigMap中的键值对导入到环境变量中有以下缺陷:
- 若配置信息过大, 可能超过环境变量的存储上限
- 若配置信息包含特殊字符, 则无法导入环境变量
K8s支持将ConfigMap挂载为volume, 只需要将volume的类型设置为ConfigMap即可. 假设我们需要将nginx的配置文件(文件名为my-nginx-config.conf)保存到ConfigMap中. 文件内容如下:
server { |
可将该文件和另一个文件(文件名为sleep-interval)放在同一目录下: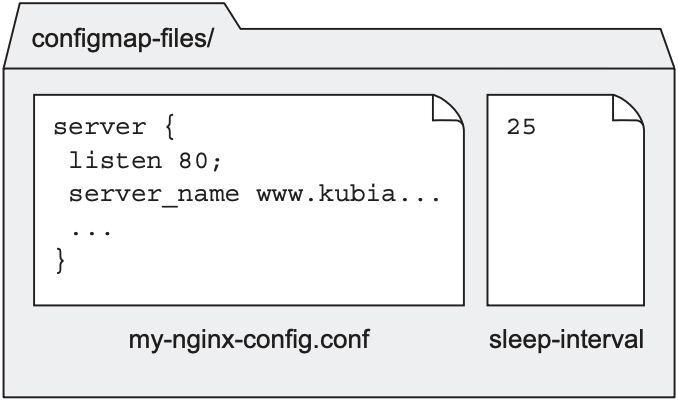
并执行kubectl create configmmap创建一个ConfigMap:
$ kubectl create configmap fortune-config --from-file=configmap-files |
当nginx需要从/etc/nginx/nginx.conf路径中加载配置时, 只需将ConfigMap挂载到指定路径上:
apiVersion: v1 |
结果如下: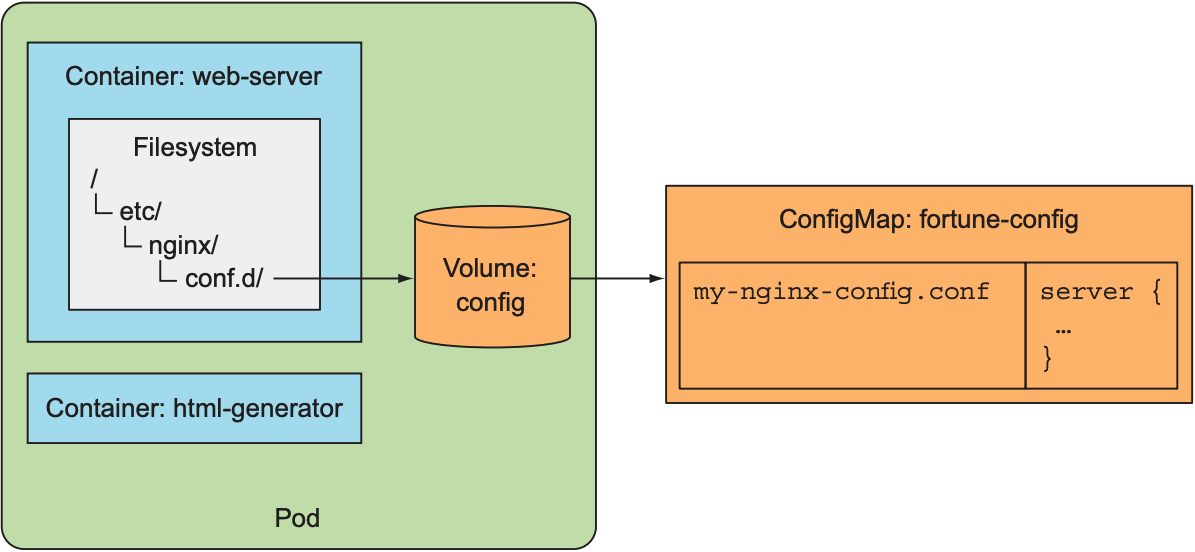
也可指定ConfigMap的某个或某几个键值对挂载到volume中:
volumes: |
需要注意的是, 将ConfigMap作为volume挂载到container时, 挂载路径上的所有文件都会被覆盖: 若/etc/nginx/conf.d存在其他文件, 则会因挂载而消失. 若不想覆盖挂载路径上的文件, 可添加subPath属性:
spec: |
这样可保证myconfig.conf挂载到container的/etc/someconfig.conf路径上, 且不会隐藏任何container已存在的文件, 如下图: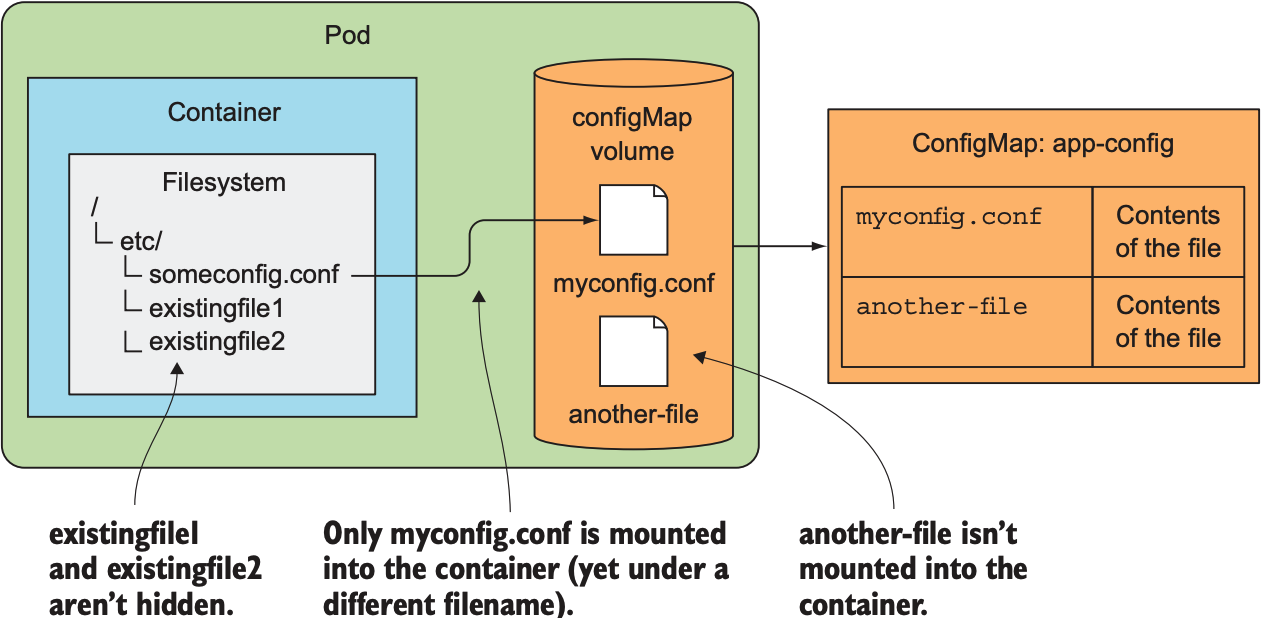
K8s还支持设置ConfigMap volume的文件权限:
volumes: |
4.6 Update Config without Restarting the App
环境变量和命令行参数的缺陷在于无法在pod运行时修改配置信息. ConfigMap volume则可以随时更新配置信息. 调用kubectl edit可修改ConfigMap:
$ kubectl edit configmap fortune-config |
由于nginx不会主动查看配置文件是否更新, 所以需要手动重启nginx:
$ kubectl exec fortune-configmap-volume -c web-server -- nginx -s reload |
ConfigMap volume的修改是原子性的, 也就是说, 即使volume中包含多个文件, container也不会读取到部分修改的文件; container要么读取到更新前的文件, 要么读取到更新后的文件. K8s通过symbolic link(软链接)实现更新操作的原子性, 如果查看volume可观察到:
$ kubectl exec fortune-configmap-volume -c web-server -- ls -lA /etc/nginx/conf.d |
配置文件sleep-interval指向data文件夹中的sleep-interval, 而data作为一个软链接指向名为4984_09_04_12_15_06.865837643的文件夹, 因此k8s会先创建一个新的文件夹, 并让data指向新的文件夹.
需要注意的是, 若使用subPath将单个文件挂载到container中, 该文件不会随着ConfigMap更新而更新; 若需要将单个文件放置在指定路径下, 可将volume挂载到其他路径上, 并在目标路径下创建一个软链接, 其指向volume的挂载路径下的指定文件.
Container的性质之一就是不变性(immutability), 因此一个image生成的多个container没有任何不同. 但若修改ConfigMap会导致container行为不同, 则破坏了这种性质. 导致这种问题的原因: container无法得知ConfigMap是否更新, 需要在程序层面检测配置文件是否更新; 若没有检测机制, 则新创建的container可能读取到新的配置信息, 从而与之前的container行为不一致. 即使container可以检测配置变动, 由于ConfigMap无法同时在多个node上更新, 因此不同container加载新配置的时间可能不同. 总而言之, 修改ConfigMap并不是一个很好的选择, 在修改前应考虑container是否可以检测变动, 是否容许container在一定时间内存在不一致行为.
5. Screts
ConfigMap提供了一个完整的配置获取方案, 但有时配置信息中包含一些敏感信息, 如密码或私有密钥. 为此K8s提供Secrets, 与ConfigMap相同, Secret也是键值对形势存储信息, 且获取键值对的方式如下:
- 将Secret的键值对作为环境变量传入container
- 将Secret作为volume挂载到pod上
K8s会将Secrets保存在master node上, 且不会加密(从Kubernetes 1.7后加密), 因此必须保证master node不会被管理员之外的人访问; K8s只会将Secrets发送给需要Secret的pod所在的node上, 且Secrets只会保留在内存中, 不会写入磁盘, 因此无需清理worker node的磁盘. 因此:
- 对于不敏感的配置信息, 放置在ConfigMap中
- 对于敏感信息, 保存在Secrets中
5.1 default token Secret
执行kubectl describe pod可查看pod绑定了哪些Secret:
$ kubectl describe pod <pod_name> |
每个pod都会自动挂载一个Secret volume, 可执行kubectl get secrets查看当前namespace下的所有Secrets:
$ kubectl get secrets |
执行kubectl describe secret可查看某个Secret的具体信息:
$ kubectl describe secret default-token-t75t5 |
可以看到, pod默认挂载的Secret包含ca.crt和token, 其用于保证pod与K8s API server之间安全通信. 执行kubectl describe pod可查看该secret的挂载位置:
... |
执行kubectl exec可查看挂载目录下的所有文件:
$ kubectl exec mypod ls /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ |
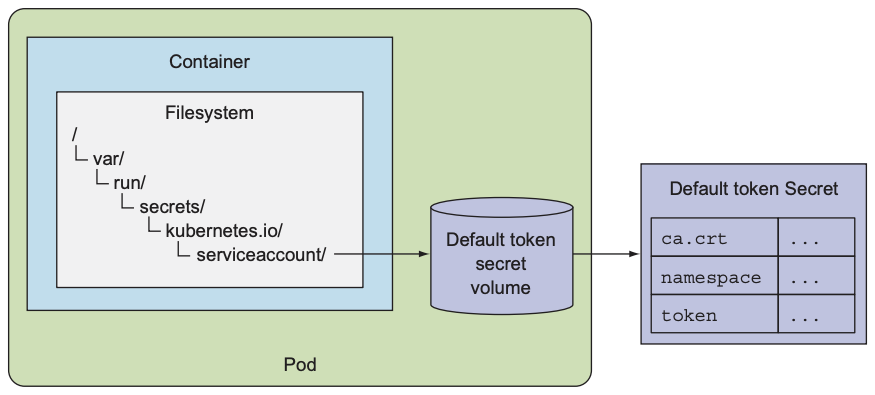
5.2 Create a Secret
以nginx为例, 若想让nginx支持HTTPS, 需要添加一个certificate(证书)和一个private key(私有密钥), 由于我们不想让所有人都看到密钥, 因此需要将它们放入一个Secret中. 以下是生成证书和密钥的指令:
$ openssl genrsa -out https.key 2048 |
再添加一个名为foo的文件, 其包含字符串bar:
$ echo bar > foo |
最后执行kubectl create secret创建一个Secret:
$ kubectl create secret generic fortune-https --from-file=https.key \ |
上述命令创建一个名为fortune-https的generic Secret, 其包含三个键值对: foo, https.key, 和https.key.
5.3 Compare ConfigMap and Secret
执行kubectl hey secret可获取secret:
$ kubectl get secret fortune-https -o yaml |
尽管ConfigMap和Secret都是键值对形式, 但两者存在以下不同:
- Secret中的键值对的key为明文形式, 但value使用Base64编码
- Secret的value不光支持纯文本, 还支持二进制
- Secret的stringData属性可让键值对以明文形式展示, 但不会被pod读取到
- 当Secret作为环境变量或volume时, container无需解码, 可直接使用键值对, 因为键值对会自动解码
5.4 Using the Secret in a Pod
为将证书和私钥传入container, 需将其挂载到container上.
apiVersion: v1 |
结果如下: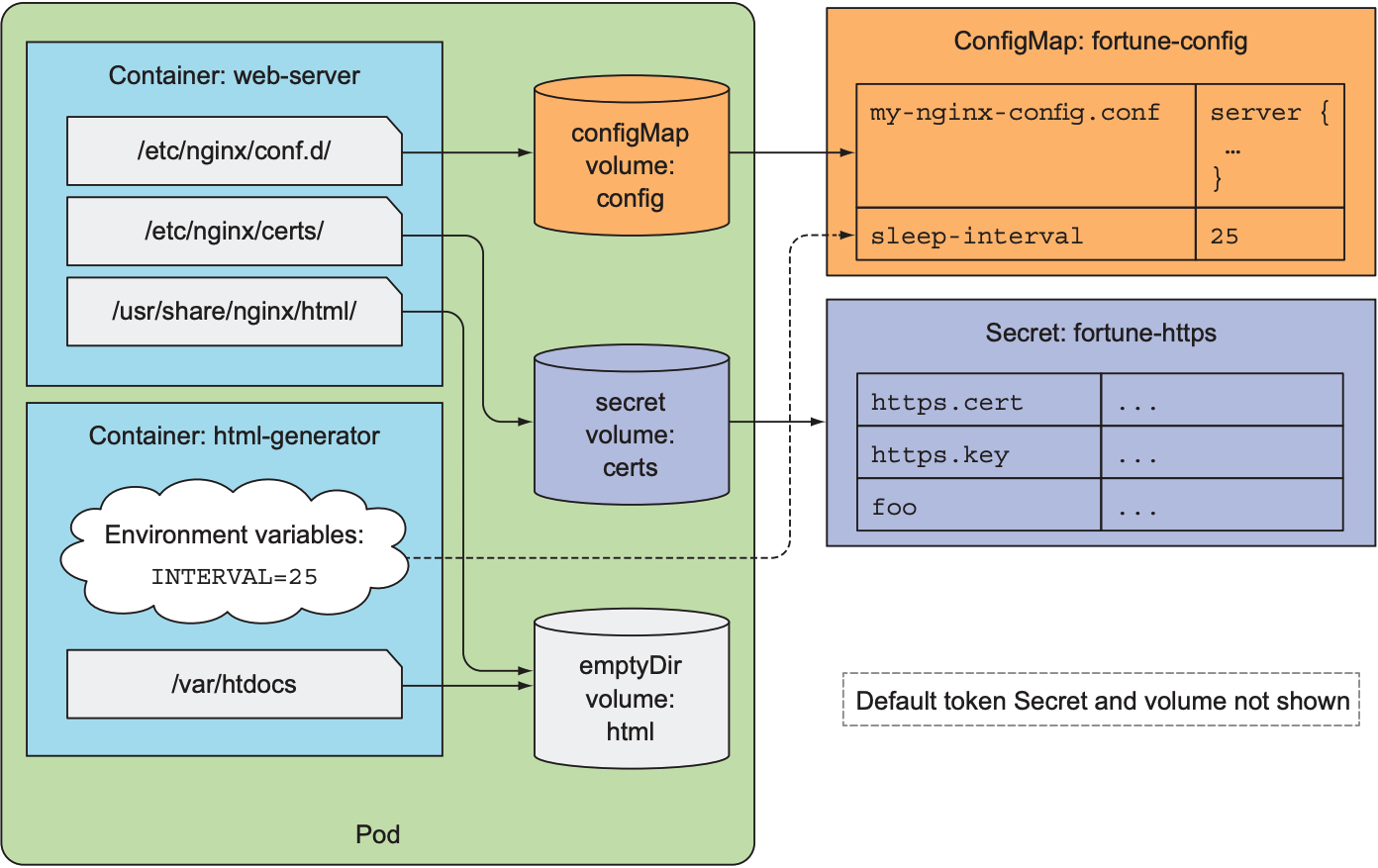
也可以将Secret导入环境变量:
... |
但并不推荐将Secret导入环境变量中, 因为很多应用都会在程序报错时将环境变量写入日志中, 从而泄漏敏感信息; 另外, 由于子进程会继承父进程的所有环境变量, 若程序需要执行第三方的程序, 也可能泄漏敏感信息.
6. Understanding image pull Secrets
上述所有image都位于public image repository中, 若需要从private image repository获取image时, 需要配置密钥:
$ kubectl create secret docker-registry mydockerhubsecret \ |
上述命令创建了一个名为mydockerhubsecret的docker-registry secret, 其会创建一个key为.dockerconfig的键值对, 用于docker login命令登陆Dockerhub.
apiVersion: v1 |