Maven
1. Introduction
Apache Maven是一个Java项目的构建和依赖管理工具, 负责管理项目的构建, 报告和文档. 以下是Maven相对于手动打包的优势:
- Maven使用artifact定义任何文件(包括jar), 且每个artifact都有一个唯一coordinate(坐标), 因此无需担心jar版本不一致或使用错误的jar
- 项目依赖外部jar时, Maven会自动下载jar所在的artifact, 并保存到repository(仓库)中, 无需开发者下载和复制粘贴jar
- Maven可自动解析jar之间的依赖关系, 无需开发者手动配置
- Maven可编译程序, 将Java文件编译为class文件
- Maven可测试代码
- Maven可将项目打包为jar或war
- Maven可部署项目
综上所述, Maven可大体分为三个方面:
- 依赖管理: Maven可负责项目中的依赖关系, 包括自动下载所需artifact并保证没有版本冲突, 依赖管理, 统一保存到repository
- 构建管理: 将源文件, 配置文件, 资源文件转化为jar或war的过程. Maven负责项目的编译, 测试, 打包, 部署, 保证每个构建步骤都遵循标准化规则
- 插件机制: Maven的所有工作都由plugin(插件)完成, 因此可以将Maven看作一个插件执行框架. 开发者可使用plugin对构建过程进行定制
以下是Maven的执行流程: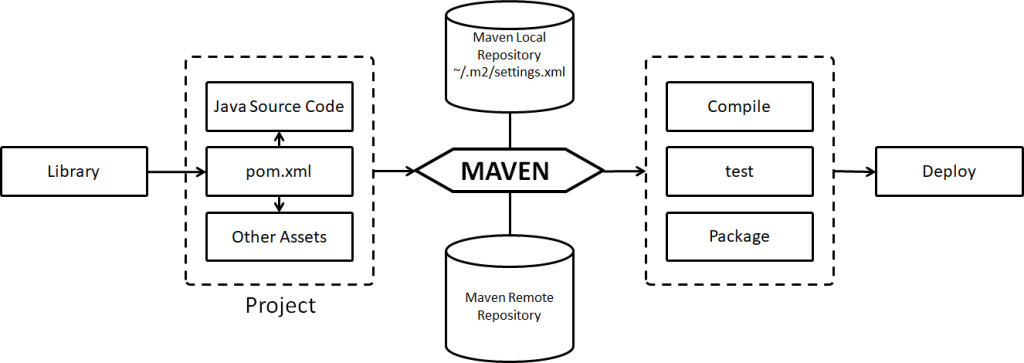
2. Standard Directory Layout
Maven中的目录结构是固定的, 通过统一的目录结构, 开发者可快速熟悉新项目. 以下是一个Maven项目的目录架构:
my-app |
以下是各个目录的说明:
| Folder | Description |
|---|---|
| src/main/java | Application/Library sources |
| src/main/resources | Application/Library resources |
| src/main/filters | Resource filter files |
| src/main/webapp | Web application sources |
| src/test/java | Test sources |
| src/test/resources | Test resources |
| src/test/filters | Test resource filter files |
| src/it | Integration Tests (primarily for plugins) |
| src/assembly | Assembly descriptors |
| src/site | Site |
| LICENSE.txt | license |
| NOTICE.txt | Notices and attributions required by libraries that the project depends on |
| README.txt | readme |
| pom.xml | Porject object model |
Maven项目中只有两个子目录: src和target:
- src目录包含用于构建项目的所有数据, 其包含两个子目录:
- main: 构建artifact的所有数据
- test: 单元测试代码
- target包含Maven构建项目后的所有输出
3. Build Lifecycle
Maven的lifecycle定义了一个构建流程, 以下是Maven内置的build lifecycle:
- default: 项目构建
- clean: 项目清理
- site: 创建项目网站
3.1 Phases of Build Lifecycle
每个build lifecycyle由多个phase(阶段)组成, 以下是default lifecycle的phases:
- validate: 验证项目是否正确, 且是否包含所有必要项
- compile: 编译项目源码, 将
.java文件编译为.class文件 - test: 使用单元测试框架测试编译后的代码
- package: 将编译后的代码大包围可分发的格式, 如JAR或WAR
- verify: 检查integration test的结果, 确保其满足要求
- install: 将package安装到local repository, 以便其作为本地其他项目的依赖项
- deploy: 将package复制到remote repository, 以便其他开发者和项目共享
除了default包含的phase, 还有两个phase经常提及:
- clean: 清理先前构建的artifact, 即删除
target目录 - site: 在
target/site下生成项目的站点文档
每个phase可指定多个goal, 但部分phase有默认goal. 当执行mvn clean命令时, 实际上顺序执行clean lifecycle的三个phase: pre-clean, clean, post-clean, 若未在POM中pre-clean和post-clean添加goal, 那么只会执行clean phase, 相当于执行mvn clean:clean.
大部分lifecycle phase都有对应的Maven命令, 使用时需注意以下几点:
mvn compile命令只编译src/main下的代码, 若需编译src/test下的代码, 可执行mvn test-compilemvn test命令会编译src/main和src/test下的代码, 并运行单元测试mvn package命令会将package保存到target下, package的命名规则为artifactId-version. 该命令会运行compile和test, 但打包后的jar或war不包含src/test下的代码
因此, lifecycle可理解为一系列build command的有序集合, 而每个command由一个或多个plugin执行.
4. POM
POM(Prject Object Model)是Maven项目中最重要的文件, 文件名为pom.xml, 该文件负责定义Maven需要做什么, 如何做. 因此该文件包含Maven项目所需的所有信息, 无需其他代码.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" |
可以看到, Maven采用declarative manifestation(声明式表现)来让开发者告诉Maven每个阶段执行什么任务. 相比Apache Ant需要开发者说明每一步的执行命令, 几乎所有任务都依赖之前执行的任务, Maven的配置容错率更高, 也更简单.
4.1 Maven Coordinate
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" |
以上是POM的最短配置, 其中groupId:artifactId:version是必填项(若parent已定义则不需要), 这三个字段构成一个artifact的coordinate.
- groupId: 表示创建该项目的组或个人, 通常是公司域名. 例如, Maven的核心artifact的groupId为
org.apache.maven. 下载artifact时, Maven会将groupId中的.替换为目录分隔符(如Unix的/), 若groupId为org.codehaus.mojo, 则artifact的保存路径为$M2_REPO/org/codehaus/mojo. - artifactId: 表示项目名称(也就是jar的名称), groupId与artifact共同组成一个artifact的编号, 用于区分不同artifact. 若groupId与上述相同, artifactId为
my-project, 则artifact的保存路径为$M2_REPO/org/codehaus/mojo/my-project. - version:
groupId:artifact负责定位到一个具体的artifact, 该参数表示artifact的版本号. 假设groupId和artifact与上述相同, version为1.0, 则保存路径为$M2_REPO/org/codehaus/mojo/my-project/1.0.
4.2 Packaging
若POM没有声明packaging标签, 则Maven默认打包为JAR. 目前有效的packaging值为pom, jar, maven-plugin, ejb, war, ear, rar. 不同packaging值下default lifecycle中的phase对应的plugin不同. 以Maven 3.9.6为例, default lifecycle中不同packaging绑定的plugin见链接.
4.3 Dependencies
Dependency是POM中最重要的部分, 也是Maven最关键的功能, 即下载和管理依赖, 并且Maven会自动引入依赖所依赖的依赖(transitive dependency, 依赖传递).
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" |
每个dependency都是当前项目的依赖项, 每个dependency可分为以下几个部分:
- groupId, artifactId, version: 这三项参数组成一个artifact的坐标, Maven根据坐标从local或remote repository查找或下载对应的artifact. 这意味着开发者所需的任何依赖都必须是artifact, 好处在于artifact都集中存放在central Maven repository, 开发者可以很方便地查找所需依赖; 坏处在于某些依赖可能因为closed-source license而无法登录central repository, 有三种方式解决:
- 使用install plugin将依赖安装到local repository:
mvn install:install-file -Dfile=non-maven-proj.jar -DgroupId=some.group -DartifactId=non-maven-proj -Dversion=1 -Dpackaging=jar - 创建一个remote repository, 使用deploy plugin将依赖部署到该repository, 这样组织或公司内的每个人都可以下载该artifact
- 将
scope设置为system, 并设置systemPath
- 使用install plugin将依赖安装到local repository:
- classifier: 该参数为可选项, 且没有固定值, 可让相同POM构建不同内容的artifact. 例如, 一个artifact可能针对Java 11和Java 1.8做了不同内容, 可配置
jdk11和jdk8生成不同内容的artifact - type: 该参数表示依赖的类型, 默认为
jar, type通常与packaging一致. - scope: 该参数表示依赖范围, 用于限制依赖项的transitivity(传递性), 一共有以下五种范围, 对应package的三个作用范围: 编译, 测试, 运行.
- compile: 默认范围, 对于三种作用范围均有效, 例如
log4j - provided: 只对编译和测试有效, 该依赖通常由外部容器提供, 运行时无需该依赖, 例如
servlet-api - runtime: 只对测试和运行有效, 如
JDBC - test: 只对测试有效, 例如
junit - system: 范围与provided一致, 该依赖由
systemPath提供, 会导致可移植性降低, 不建议使用
- compile: 默认范围, 对于三种作用范围均有效, 例如
- systemPath: 仅当scope为system时才使用该参数, 否则报错. 该参数值必须是一个绝对路径, 建议使用property来指定一个机器特定的路径, 例如
${java.home}/lib - optional: 当当前项目本身作为一个依赖时, 可将该参数设置为true. 例如, 项目A依赖于项目B来编译一部分运行时不会使用的代码, 而项目X依赖于项目A时可能不需要安装项目B, 因此A可将B设置为optional
以下是Maven dependency下载失败的几个原因:
- 下载依赖时出现网络故障或Maven repository宕机, 导致无法链接到repository: 检查网络和Maven repository
- 依赖的版本号错误, 或依赖项没有正确定义, 导致Maven下载错误的依赖项: 检查POM中的dependency是否设置正确
- Local Maven repository损坏, 导致Maven无法正确使用现有依赖项: 清理本地缓存
4.4 Build
默认情况下, 构建项目无需额外配置, Maven已有对应的缺省配置, 若需自定义某些配置, 如修改打包文件的名称, 打包时排除部分文件, 或使用其他plugin, 可修改pom.xml中的build元素. POM 4.0.0标准下, build元素会出现在两个元素下: project和profiles, 为区分这两者, 可称为porject build和profile build.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" |
有些元素可出现在project build和profile build中, 有些则不能, 因此build中的元素分为两种:
- BaseBuild类型元素: 可出现在
project build或profile build中 - Build类型元素: 只出现在
project build中
4.4.1 BaseBuild Elements
<build> |
- finalName: 项目打包后的名称, 默认为
artifactId-version - defaultGoal: 若没有给出执行的目标或phase(如命令
mvn), 则将该参数作为默认目标 - directory: Maven构建时生成文件的存放目录, 默认为
${project.basedir}/target - filter: 存放
*.properties文件的目录, 默认为${project.basedir}/src/main/filters/ - resources: 指定资源位置, 并在打包时将其放入项目特定位置, 如下:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<build>
...
<resources>
<resource>
<targetPath>META-INF/plexus</targetPath>
<filtering>false</filtering>
<directory>/home/workspace/aven_maven-box_maven-site_master/src/main/plexus</directory>
<includes>
<include>configuration.xml</include>
</includes>
<excludes>
<exclude>**/*.properties</exclude>
</excludes>
</resource>
</resources>
<testResources>
...
</testResources>
...
</build>
</project>- resources: resource元素列表, 每个
resource元素对应一种资源 - targetPath: 用于放置资源的目录, 默认为base directory
- filtering: 是否过滤资源, 可设置为true或false
- directory: 指定资源的父目录, 默认为
${project.basedir}/src/main/resources - includes: 资源文件的匹配模式, 通常使用
*作为通配符指定资源文件 - excludes: 需忽略的文件模式, 若
includes和exclude冲突, 则排除该资源文件 - testResources: testResource元素列表,
testResource元素的定义与resource元素相同, 但只有test阶段使用, 且默认防止目录为${project.basedir}/src/test/resources
- resources: resource元素列表, 每个
- plugins: Maven可看作一系列plugin的执行框架, 除了Maven自带的plugin, 开发者也可添加其他plugin, 从而在构建时运行自定义操作, 以下是plugin例子:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<build>
...
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.6</version>
<extensions>false</extensions>
<inherited>true</inherited>
<configuration>
<classifier>test</classifier>
</configuration>
<dependencies>...</dependencies>
<executions>...</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>- groupId:artifactId:version: plugin的坐标信息
- extensions:
true或false, 是否加载该plugin的拓展, 默认为false - inherited:
true或false, 该plugin配置是否应用于继承自该plugin的POM - configuration: plugin的配置信息, 特定于各个插件
- executions: 由于一个phase可包含多个goal, 该参数可在运行到某个
phase时, 执行该plugin的一个或多个goal- id: execution的id, 执行到当前execution时输出
[plugin:goal execution: id] - goals: 该plugin中将要执行的goal
- phase: 执行到该phase时运行该plugin
- inherited: 如上
- configuration: 如上
- id: execution的id, 执行到当前execution时输出
- pluginManagement: 该元素也可包含
plugin元素, 但该元素内的所有plugin也会被child POM继承
4.4.2 Build Element
Build类型的元素只出现在project build中,
- Directories: 为整个POM设置特定目录结构, 如下:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
...
<build>
<sourceDirectory>/home/jenkins/82467a7c/workspace/aven_maven-box_maven-site_master/src/main/java</sourceDirectory>
<scriptSourceDirectory>/home/jenkins/82467a7c/workspace/aven_maven-box_maven-site_master/src/main/scripts</scriptSourceDirectory>
<testSourceDirectory>/home/jenkins/82467a7c/workspace/aven_maven-box_maven-site_master/src/test/java</testSourceDirectory>
<outputDirectory>/home/jenkins/82467a7c/workspace/aven_maven-box_maven-site_master/target/classes</outputDirectory>
<testOutputDirectory>/home/jenkins/82467a7c/workspace/aven_maven-box_maven-site_master/target/test-classes</testOutputDirectory>
...
</build>
</project> - Extensions: 该元素中的
extension会被添加到Maven build的classpath中, 但不会打包到最终的artifact中. 因此, extension很适合用于指定公共plugin接口的其中一个实现, 如下:<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
...
<build>
...
<extensions>
<extension>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.wagon</groupId>
<artifactId>wagon-ftp</artifactId>
<version>1.0-alpha-3</version>
</extension>
</extensions>
...
</build>
</project>
5. Transitive Dependencies
依赖管理作为Maven的核心功能, 可帮助开发者定义, 创建和维护具有明确定义的classpath和库版本, 并实现可重复性构建. 当开发者添加依赖时, Maven会自动添加依赖所需的库. 假设项目A依赖于B, B依赖于C, 可写作A->B->C, 当构建项目A时, Maven会自动下载B和C, 并导入到jar包, 称为Transitive Dependencies(依赖传递). Maven没有设置依赖的数量上限和深度上限, 唯一需要注意的是cyclic dependency(循环依赖).
5.1 Dependency Mediation
由于依赖传递会自动下载所有依赖, 项目的依赖树会变得非常大, 因此当一个artifact的多个版本作为依赖时, Maven会选择最短依赖路径的版本; 若路径长度一致, 则选择先被声明的依赖版本, 例如:
A |
上图中A依赖于两个版本的D, 但由于A从E到D的依赖路径更短, 因此选择D的1.0版本, 若需指定2.0版本, 可在POM中显式声明:
A |
下图中, A到D的两条路径长度一致, 由于B在POM中先被声明, 因此选择D的2.0版本:
A |
5.2 Dependency Management
除了Maven自行选择依赖的版本号, 开发者也可在dependencyManagement中指定依赖的版本, 从而直接控制依赖传递.
<project> |
5.3 Dependency Scope
通过设置依赖范围(dependency中的scope元素)减少jar包中的不必要依赖
5.4 Excluded Dependencies
开发者可通过dependency中的exclusion元素排除某个特定依赖.
<project> |
5.5 Optional Dependencies
若项目Y依赖于Z, Y的开发者可将Z设置为optional, 当X依赖于Y时, X不会依赖于Z, 相当于默认排除Z的依赖
<project> |
6. Inheritance
Maven的inheritance(继承)允许一个项目从另一个项目中继承配置信息, 从此多个项目可共享同一配置信息, 以下是继承的优点:
- 将大型项目拆分为多个模块
- 一个大型project下存在多个module
- 每个module都有自己的依赖信息
由于同属一个project, 因此多个module可能存在共同的依赖, 且项目内的依赖版本需一致, 可使用parent POM统一管理信息. 以下是一个最简单的parent POM:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" |
Parent POM的packgaing元素必须为pom, 以下是parent POM会被继承到child POM的元素:
- groupId
- version
- description
- url
- inceptionYear
- organization
- licenses
- developers
- contributors
- mailingLists
- scm
- issueManagement
- ciManagement
- properties
- dependencyManagement
- dependencies
- repositories
- pluginRepositories
- build
- plugin executions with matching ids
- plugin configuration
- reporting
需要注意的是, child POM会自动继承groupId和version, 因此child POM只需设置artifactId. Parent POM中dependencies的所有依赖都会继承到child POM, 因此子项目可直接调用该依赖; 但一般不会直接在parent POM中使用dependencies, 而是使用dependencyManagement: 当parent POM设置dependencyManagement后, child POM不会自动添加该依赖, 只有显式声明相同groupId和artifactId时才会拥有该依赖, version会从parent POM继承而来.