Bucket Sort
Bucket Sort
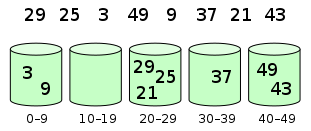
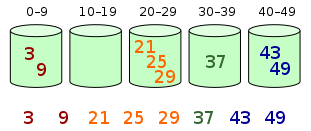
Bucket sort先将元素分配到多个bucket, 再通过不同的排序算法或递归应用bucket sort来实现对每个bucket内元素的排序. 该算法的时间复杂度取决于: bucket内的元素排序, bucket数量, 输入元素是否分布均匀. 以下是bucket sort的算法步骤:
- 初始化多个bucket
- 遍历原始数组, 将每个元素分配到不同bucket中
- 对非空bucket内的元素排序
- 依次访问bucket, 并将元素放回数组
451. Sort Characters By Frequency
Given a string s, sort it in decreasing order based on the frequency of the characters. The frequency of a character is the number of times it appears in the string.
Return the sorted string. If there are multiple answers, return any of them.
Example 1:
Input: s = "tree" |
Bucket Sort
字符串的字符范围为ascii子集, 每个字符的出现次数为[0, Length_of_string], 题目要求字符按照出现频率从小到大排列, 因此可使用bucket sort. 步骤如下:
- 遍历字符串, 将每个字符的出现次数记录在
count数组中 - 遍历
count, 将每个出现次数对应的字符记录在alpha数组中 - 从小到大遍历
alpha, 将每个字符保存在结果中
class Solution { |
347. Top K Frequent Elements
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return the k most frequent elements. You may return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2 |
Bucket Sort
思路与上一题相同, 先统计每个数字出现的频率, 再将相同频率的数字放入一个集合中, 最后按照频率从大到小取出数字.
class Solution { |
220. Contains Duplicate III
You are given an integer array nums and two integers indexDiff and valueDiff.
Find a pair of indices (i, j) such that:
i != jabs(i - j) <= indexDiffabs(nums[i] - nums[j]) <= valueDiff
Return true if such pair exists or false otherwise.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,1], indexDiff = 3, valueDiff = 0 |
Slide Window + Bucket Sort
题目对数组内的任意两个元素(nums[i]与nums[j])有两点要求:
abs(i - j) <= indexDiffabs(nums[i] - nums[j]) <= valueDiff
对于第一点要求, 可通过slide window不断添加新的元素, 并删除范围之外的旧元素; 对于第二点要求, 可将每个元素放入bucket: 假设数组内元素为0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, valueDiff为3, 让每个元素除以valueDiff + 1后, 数组变为0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 可以发现, 前四个元素为0, 接下来四个元素为1, 每四个元素作为一个bucket, 每个bucket内的最大差值为valueDiff, 因此:
- 若两个数字处于同一bucket, 则其差值必小于或等于valueDiff
- 若两个数字处于相邻bucket, 则其差值可能小于或等于valueDiff
- 若两个数字对应的bucket间隔一个或多个bucket, 则其差值必大于valueDiff
需要注意的是, 由于0不属于正值或负值, 假设valueDiff为3, 则0与1,2,3处于同一bucket, 也与-1,-2,-3处于同一bucket, 因此需特殊处理负值的bucket.
class Solution { |