Name and Address Conversions
1. Domain Name Syste (DNS)
DNS用于映射hostname和IP address. hostname可以是简单的solaris或freebsd, 或FQDN(fully qualified domain name), 例如solaris.unpbook.com.
FQDN也称为absolute name, 必须以句号结尾(punctuation mark), DNA用户通常会忽略最后的句号. 最后的句号用于通知resolver这是一个FQDN, 无需搜索可能的所有domain.
1.1 Resource Records
DNS中的entry被称为resource record(RR), 以下是几种常见的RR:
- A: A record将hostname映射为32-bit IPv4 address. 对于host为freebsd, domain为unpbook.com, 其A record为:
freebsd IN A 12.106.32.254
IN AAAA 3ffe:b80:1f8d:1:a00:20ff:fea7:686b
IN MX 5 freebsd.unpbook.com.
IN MX 10 mailhost.unpbook.com. - AAAA: AAAA record将hostname映射为128-bit IPv6 address. AAAA表示4倍的32-bit address, 也就是128-bit address
- PTR: PTR record将IP address映射为hostname. 例如: 对于freebsd host, 其两个PTR为
254.32.106.12.in-addr.arpa和b.6.8.6.7.a.e.f.f.f.0.2.0.0.a.0.1.0.0.0.d.8.f.1.0.8.b.0.e.f.f.3.ip6.arpa - MX: MX record标注某个host作为mail exchanger. 一个host可有多个MX record, 每个MX record有不同preference value, 按照从小到大排序.
- CNAME: canonical name, 将一个hostname映射为另一个hostname.
1.2 Resolvers and Name Server
Name server会运行network service, 保存DNS record, 并回应请求. 而被client和server用于与name server通信的工具称为resolver, 通常为gethostbyname()和gethostbyaddr(), 前者用于将hostname映射为IPv4 address, 后者用于将IPv4 address映射为hostname.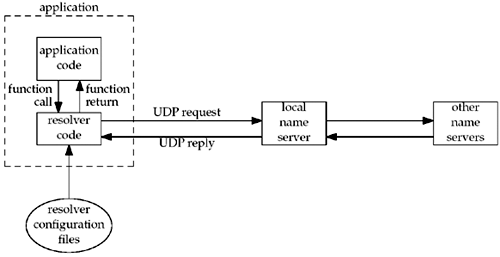
上图表示application, resolver和name server之间的关系. 对于用户来说, 只需要在application code中调用resolver APIs即可. Resolver code会读取系统中的configuration file决定从哪个name server获取record, local name server的IP address通常保存在/etc/resolv.conf文件中. Local name server接收到请求后, 如果回复准确答案, 则向更高级的name serber发送请求. 通常情况下, DNS请求和回复为UDP, 如果数据过大, 会自动切换为TCP.
1.3 DNS Alternatives
在不使用DNS的情况, 也可以通过static host file(通常为/etc/hosts文件), NIS(Network Information System)或LDAP(Lightweight Directory Access Protocol)获取hostname和IP address. 但尤其每个系统实现不用, 使用的方法也有所不同, 因此需要通过resolver functions作为统一解决方案.
2. gethostbyname Function
无论调用connect()还是sendto(), 都需要知道对端的IP address, 但IP address不好记忆, 尤其是IPv6 address, 且随时可能更改, 因此需要通过将hostname映射为对应的IP address.
|
gethostbyname()只返回IPv4 address, 因此该函数会随着IPv6的普及而逐渐消失, 推荐使用getaddrinfo()代替. 以下是hostent的结构图: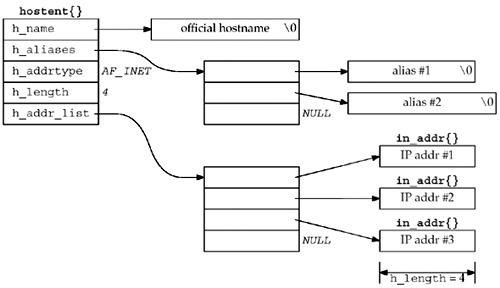
其中, h_name表示host的canonical name. 例如: 当对solaris调用gethostbyname()时, 其FQDN为solaris.unpbook.com, 也就是其canonical name. 不同于其他socket function, 出错时gethostbyname()不会设置errno, 而是在h_errno上设置以下常量:
- HOST_NOT_FOUND: 找不到host
- TRY_AGAIN: name server发生临时错误, 需要重新发送请求
- NO_RECOVERY: name server发生不可恢复的错误
- NO_DATA: host存在, 但name server中没有对应的IP address, 例如hostname只有MX record
3. gethostbyaddr Function
gethostbyaddr()用于将IPv4 address映射为hostname, 与gethostbyname()功能相反.
|
4. getservbyname and getservbyport Functions
Service和host一样, 都可以通过name标记, 每个service都有自己的name和port number, 因此查找一个service即可通过其name, 也可以通过port number.
|
以下程序使用gethostbyname()和getservbyname()来实现一个简易client:
/* first command-line argument: hostname |
5. getaddrinfo Function
gethostbyname()和gethostbyaddr()不支持IPv4, 如果需要解析IPv6 address, 需要使用getaddrinfo()实现name-to-address和service-to-port, 定义于POSIX specification.
struct addrinfo { |
其中, ai_flags的可选项如下:
- AI_PASSIVE: 若设置该flag, 则result返回的address应能用于
bin(),listen(), 或accept(), 也就是说, 该address用于passive socket. - AI_NUMERICHOST: 让
getaddrinfo()返回canonical name - AI_NUMERICSERV: hostname参数必须为address string, 不能为hostname
- AI_V4MAPPED: 该option一般与
ai_family设置为AF_INET6一同使用, 保证AAAA record无法找到时返回A record. - AI_ALL: 与AI_V4MAPPED一同使用, 返回hostname下的A record和AAAA record.
- AI_ADDRCONFIG: 若存在多个端口, 只返回给定IP version的IP address.
hints参数中除了ai_flags, 还可修改其他属性:
- ai_family
- ai_socktype
- ai_protocol
若hints为NULL, 则ai_flags, ai_socktype, ai_protocol都为0, 且ai_family为AF_UNSPEC.getaddrinfo()返回一个链表, 其中每个node都表示一个addrinfo structure, 以下两种情况会导致返回多个nodes:
- hostname下存在多个addresses, 每个addrinfo structure包含一个address
- service下存在多个socket type, 每个addrinfo strcuture包含一种socket type
假设某一host下有两个IP address, 有4个addrinfo structures返回:
- 第一个IP address且socket type为
SOCK_STREAM - 第一个IP address且socket type为
SOCK_DGRAM - 第二个IP address且socket type为
SOCK_STREAM - 第二个IP address且socket type为
SOCK_DGRAM
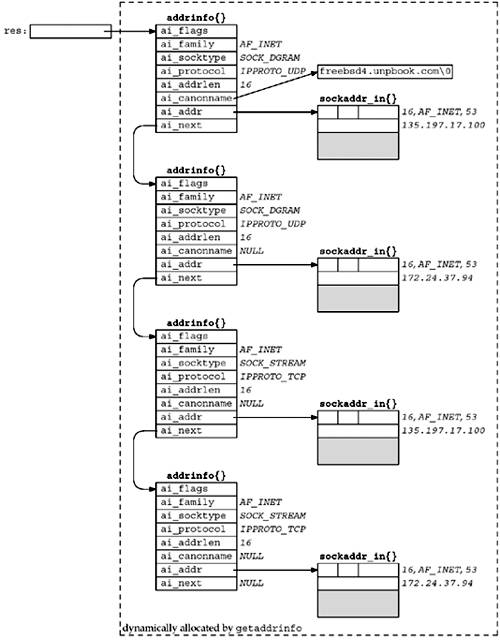
若hints参数中设置了AI_CANONNAME flag, 返回的第一个addrinfo中的ai_canonname会返回host的canonical name. hints参数中的ai_protocol可选项如下:
- IPPROTO_IP: 0
- IPPROTO_IPV4: 4
- IPPROTO_IPV6: 41
- IPPROTO_UDP: 17
- IPPROTO_TCP: 6
ai_socktype的可选项如下:
- 0: any type of socket type can be returned
- SOCK_STREAM: connection-based byte stream
- SOCK_DGRAM: connectionless, unreliable datagram
以下是不同service和ai_socktype下addrinfo structure的返回数量:
| ai_socktype | TCP only | UDP only | TCP and UDP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| SOCK_STREAM | 1 | error | 1 |
| SOCK_DGRAM | error | 1 | 1 |
getaddrinfo()主要用于以下方法:
- 可被TCP或UDP client用于解析hostname和service. TCP client会调用
socket()和connect()遍历所有IP addresses, 直到成功连接某个IP address; UDP client也可以使用sendto()或connect()尝试向多个IP address发送请求. - 若client只需要处理特定socket type, 则可以通过hint参数中的ai_socktype标记socket type
- server一般会指定service, 并将hostname置为NULL, 且在hints参数中标记
AI_PASSIVEflag, 返回的socket address structure应该包含INADDR_ANY(Ipv4)或IN6ADDR_ANY_INIT(IPv6) - 若server调用
recvfrom()获得client的socket address structure, 其中ai_addrlen表示大小 - 若server只处理特定socket type, 可使用hints参数中的ai_socktype指定socket type
- TCP和UDP server可使用
select()或poll()对getaddrinfo()返回的每个IP address分别创建listening socket
6. gai_strerror Function
gai_strerror()可将getaddrinfo()返回的错误值转换为响应字符串
|
7. freeaddrinfo Function
getaddrinfo()中的addrinfo structure是动态分配的, 这时需要调用freeaddrinfo()释放内存.
|
8. getaddrinfo Function: IPv6
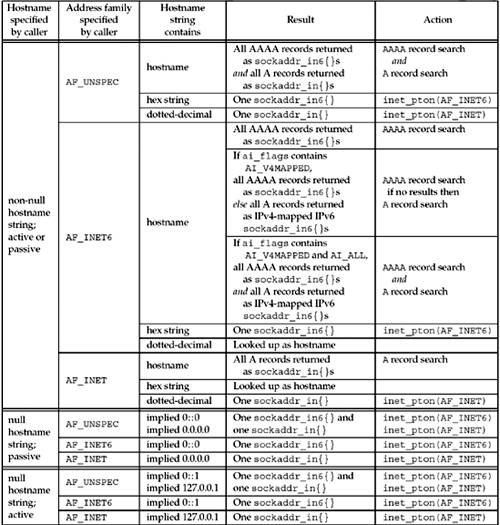
getaddrinfo()主要应对两种输入: socket address structure的类型, 需要从DNS或其他数据库中搜索的record类型hints参数中的ai_family表示返回的socket address structure类型. 若ai_family为AF_INET, 则返回的addrinfo structure中的ai_addr不能为sockaddr_in6; 同理, 若ai_family为AF_INET6, 则不能返回sockaddr_in.- 若
hints参数中的ai_family为AF_UNSPEC, 则返回所有查到的protocol family - 若ai_flags设置了AI_PASSIVE且没有设置hostname, 则在sockaddr_in6中返回IPv6 wildcard address(IN6ADDR_ANY_INIT), sockaddr_in structure中返回 IPv4 wildcard address(INADDR_ANY)
- hints参数中的ai_family和ai_flags用于标识搜索DNS中的record类型和返回的地址类型, 如上图表格所示.
- hostname可谓IPv6 hex string或IPv4 dotted-decimal string, 但必须与ai_family匹配: IPv6 hex string不能与AF_INET一起输入, IPv4 dotted-decimal string和AF_INET6不能一起输入, 但AF_UNSPEC可以与任何IP address组合.
9. getaddrinfo Function: Examples
假设某程序使用getaddrinfo(), 并可接收以下参数: hostname, service name, address family, socket type, AI_CANONNAME flag. 其中, -f表示address family, -c表示canonical name, -h表示hostname, -s表示service name, -t表示socket type.
% testga -f inet -c -h freebsd4 -s domain |
也可以指定socket type来获取host上的所有IPv4 addresses:
% testga -f inet -t stream -h gateway.tuc.noao.edu -s daytime |
通过不指定address family, 可获取host上的所有IPv4和IPv6 address:
freebsd % testga -h aix -s ftp -t stream |
通过设置AI_PASSIVE flag可获取wildcard address:
% testga -p -s 8888 -t stream |
10. host_serv Function
host_serv()可让调用者在不必生成hints structure的前提下调用getaddrinfo()
struct addrinfo *host_serv(const char *host, const char *serv, |
11. tcp_connect Function
tcp_connect()可通过hostname获取server IP address并建立连接.
int tcp_connect(const char *host, const char *serv) |
12. tcp_listen Function
int tcp_listen(const char *host, const char *serv, |
13. udp_client Function
int udp_client(const char *host, const char *serv, SA **saptr, |
14. udp_connect Function
int udp_connect(const char *host, const char *serv) |
15. udp_server Function
int |
16. getnameinfo Function
|
17. Re-entrant Functions
Reentrant function意味着函数运行中途被打断后不会影响之前的程序运转. reentrant需要遵循以下几个原则:
- 尽量不要使用global和static变量. 尽管有方法防止global和static变量影响程序, 但有时也会造成不可知的影响
- 运行时不可修改代码
- 程序内不可运行non-reentrant function
gethostbyname()和gethostbyaddr()都不是re-entrant functions, 因为这两个函数共享static variable:
static struct hostent host; /* result stored here */ |
假设进程运行gethostbyname()时被signal打断, signal handler中运行gethostbyaddr()导致host变量被覆盖, 造成reentrancy problem. 关于reentrant function的总结如下:
gethostbyname(),gethostbyaddr(),getservbyname(),getservbyport()为non-renentrant function, 因为使用static structure.- 部分系统为以上4个函数提供了reentrant functions, 以
_r为后缀 inet_pton()和inet_ntop()为reentrant functionsinet_ntoa()为non-reentrant function, 部分UNIX系统会提供reentrant versiongetnameinfo()只有在调用reentrant function时才可能为reentrant functionerrno是一个线程共享的global variable, 因此需要在signal handler开始时保存errno, 退出时恢复errno
18. gethostbyname_r and gethostbyaddr_r Functions
Linux和Solaris都提供了name-to-address和address-toname的reentrant functions:
int gethostbyname_r(const char *hostname, struct hostent *result, |
可以看到, 这两个functions都多了很多参数. buf由调用者申请空间, 用于保存canonical hostname, buflen为buf的大小. 虽然没有规定buf应为多少, 但通常设置为8192 bytes可满足绝大多数hostname; 当发生错误时, 错误码保存在h_errnop. 需要注意的是, 并不是所有系统支持reentrancy的gethostbyname()和gethostbyaddr(), UNIX 98和POSIX specification中这两个function不需要thread-safe或reentrant.
19. Obsolete IPv6 Address Lookup Functions
19.1 RES_USE_INET6 Constant
由于gethostbyname()无法指定address family, 所以引入RES_USE_INET6 constant来指定address family. 开启RES_USE_INET6后, gethostbyname()会优先搜索AAAA record, 若没有AAAA record, 再查看A record. 由于hostent只有一个address length, 所以gethostbyname()只能返回IPv6或IPv4 address. RES_USE_INET6也可以返回IPv4-mapped IPv6 adddress.
19.2 gethostbyname2 Function
|
19.3 getipnodebyname Function
RES_USE_INET6和gethostbyname2()已在RFC 2553废弃, 因为RES_USE_INET6是一个global constant. 因此引入getipnodebyname()解决IPv6 address问题.
|
getipnodebyname()和getipnodebyaddr()已在RFC 3493废弃.
20. Other Networking Information
上述所有函数主要围绕4类信息: host. network, protocol, service. 这4类信息都保存在各自文件中, 可通过以下函数获取:
- getXXXent functions: 打开并读取文件中的一个entry
- setXXXent functions: 打开并回到文件头部
- endXXXent functions: 关闭文件
struct hostent *gethostent(void); |
每个函数都定义了自己的structure: hostent, netent, protoent, servent. 除了get, set, end functions, 还有一类函数称为keyed lookup functions, 其名字一般为getXXXbyYYY, keyed lookup function不会返回文件中的每个entry, 而是根据参数的要求匹配相应的entry.
| Information | Data file | Structure | Keyed lookup functions |
| Hosts | /etc/hosts | hostent | gethostbyaddr, gethostbyname |
| Networks | /etc/networks | netent | getnetbyaddr, getnetbyname |
| Protocols | /etc/protocols | protoent | getprotobyname, getprotobynumber |
| Services | /etc/services | servent | getservbyname, getservbyport |
使用DNS的条件如下:
- host和network需要通过网络发送DNS请求获取, protocl和service则需要通过本机文件获取.
- 当需要获取host和network时, 只能通过keyed lookup function查询. 而不能用
gethostent()获取